How BIM is Enhancing Urban Design: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is emerging as a transformative force in the dynamic realm of urban development. BIM goes beyond conventional design methods and offers a holistic approach that fosters sustainability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in urban environments. BIM serves as a collaborative platform for urban designers, seamlessly integrating stakeholders into urban development projects.
Read the blog to explore the impact of BIM urban design and how it is shaping the future of cities, where innovative technology converges with urban design principles to create resilient and interconnected communities. Let’s get started!
Why The World Needs Urban Designers
Urban designers play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of our expanding urban environments. Tasked with crafting city layouts that balance functionality, aesthetics, and sustainability, they contribute to the creation of cohesive, resilient urban spaces. Urban designers consider factors like transportation, housing, green spaces, and community infrastructure, aiming to enhance overall life quality.
As cities confront issues such as overpopulation, climate change, and social inequality, urban designers emerge as crucial problem-solvers. Their expertise aids in developing solutions to problems like traffic congestion, pollution, and insufficient public spaces, fostering sustainable and inclusive urban growth. In this fast-growing urbanisation, the role of urban designers is important in shaping cities to be not only efficient and visually appealing but also adaptable to the evolving needs and challenges of the coming years.
Role of BIM in Urban Design

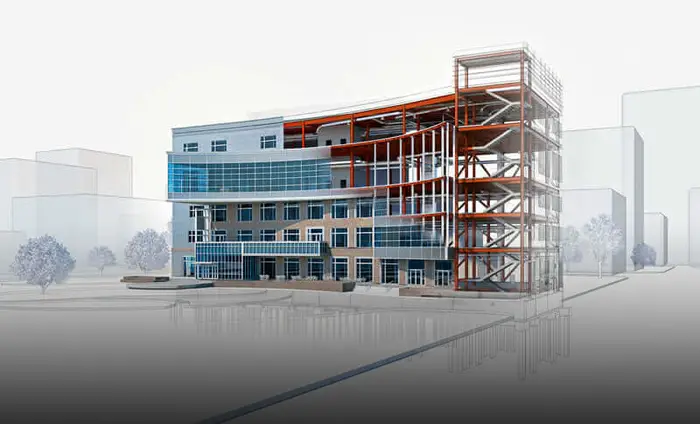
BIM plays a pivotal role in revolutionising urban design by offering a comprehensive and collaborative approach to the entire project lifecycle. BIM serves as a digital backbone, fostering efficiency, accuracy, and communication among diverse stakeholders in the urban design process.
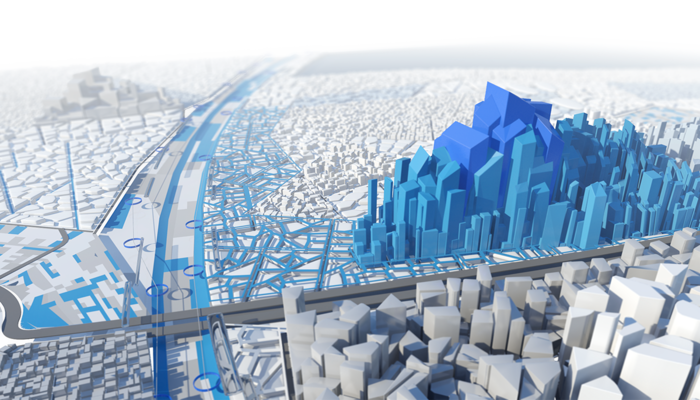
In the initial stages, BIM facilitates precise site analysis and visualisation, allowing urban designers to create detailed 3D models of the existing environment. This aids in informed decision-making regarding spatial relationships, zoning, and land use. As projects progress, BIM supports collaborative design by enabling seamless communication and coordination among architects, engineers, and planners. Real-time updates and shared information enhance teamwork, reducing errors and optimising design outcomes.
BIM's ability to integrate data on energy consumption, material usage, and environmental impact contributes to sustainable urban design. It empowers designers to make environmentally conscious decisions, aligning projects with modern sustainability goals. In essence, BIM is a transformative tool for urban designers, offering a holistic, data-driven approach that enhances efficiency, collaboration, and sustainability throughout the urban design process.
Popular BIM Software and Tools
BIM software and tools allow architects, engineers, and urban planners to create, manage, and visualise complex projects. All these tools have different strengths, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the urban design project and the preferences of the design team. Many professionals use a combination of these tools to leverage their unique features throughout the urban design process. Here are some popular BIM software and tools used in urban design:
1. Autodesk Revit
Revit is a versatile BIM software that supports the entire building lifecycle, enabling users to create 3D models with parametric design elements. It facilitates collaboration among disciplines and is commonly used in urban design for detailed building models, project data management, and stakeholder coordination. Its parametric modelling capabilities are particularly useful in designing complex urban structures.
2. ArchiCAD
ArchiCAD is a robust BIM tool for architectural design, offering 3D modelling, documentation, and collaboration features. It uses a "virtual building" approach, allowing users to work with a virtual representation of the actual building. Ideal for urban design projects, ArchiCAD facilitates close collaboration between professionals, making it valuable in the early stages of urban planning.
3. VectorWorks Architect
VectorWorks Architect is a versatile tool that integrates 2D drafting, 3D modelling, and BIM functionality, making it ideal for urban design. It supports collaboration and integrates seamlessly with other VectorWorks design products, enabling the creation of holistic urban designs.
4. Bentley’s AECOsim
The Bentley’s AECOsim Building Designer is a BIM tool that aids in architectural, structural, and MEP design, promoting interdisciplinary collaboration and offering simulation and analysis tools. It is ideal for large-scale urban projects and its integration with other Bentley products enhances its use in infrastructure-focused urban design.
5. Rhino/Grasshopper
Rhino is a 3D modelling tool and Grasshopper is a visual programming language plugin that enables parametric and algorithmic design. These tools are particularly useful in urban design for creating complex models, exploring design variations, and optimising urban spaces based on specific parameters.
Benefits of BIM in Urban Design
BIM promotes collaboration, accuracy, early error detection, and reduced inconvenience and project delays. It represents a shift towards data-driven planning and construction, enhancing collaboration, accuracy, and increased sustainability. BIM's use of urban design represents a paradigm shift towards integrated and data-driven approaches.
1. Greater Accuracy
BIM allows for the creation of detailed and accurate 3D models that represent the entire urban environment. This level of precision helps in making informed decisions and reduces the likelihood of design discrepancies.
Example: An accurate BIM model can assist in analysing the impact of proposed developments on existing structures, utilities, and landscapes, ensuring that new additions fit seamlessly into the urban fabric.
2. Early Error Detection
BIM enables the identification of potential clashes and conflicts within the design at an early stage. This early detection helps in resolving issues before they become costly problems during construction.
Example: Clash detection in BIM can identify conflicts between different building components or utilities, preventing issues such as underground infrastructure clashes or spatial conflicts between buildings.
3. Reduced Project Delays
BIM allows for better project visualisation which helps stakeholders understand the design intent. This transparency can reduce uncertainty and minimise disruptions during construction.
Example: By using BIM to model the phasing of a construction project, urban planners can communicate and visualise how different stages will impact traffic, pedestrian flow, and public spaces. This allows for proactive measures to minimise inconvenience.
4. Increased Sustainability
BIM supports sustainable urban design by allowing for the analysis of environmental factors, energy efficiency, and life cycle assessments.
Example: BIM simulates and analyses the environmental performance of buildings and infrastructure, helping designers make informed decisions about materials, energy usage, and waste management to create more sustainable urban environments.
Challenges in Urban Renewal and BIM Solutions
BIM overcomes challenges in urban renewal projects by improving project management, communication, and decision-making. Its ability to integrate data, streamline workflows, and enhance collaboration contributes to more efficient and successful urban renewal endeavours.
1. Time Constraints
Challenge: Urban renewal projects often face tight timelines due to the need for quick transformations in response to changing urban needs.
BIM Solution: BIM facilitates faster project timelines by enabling concurrent design and construction activities. Design changes are implemented seamlessly, and 4D BIM (time-based scheduling) aids in visualising and optimising construction sequences, improving overall project efficiency.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Challenge: Urban renewal projects must adhere to various regulations, zoning codes, and environmental standards, adding complexity to the planning and design process.
BIM Solution: BIM allows for better regulatory compliance by incorporating rule-based design checks. This ensures that the design aligns with local codes and regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance issues during construction.
3. Data Management
Challenge: The vast amount of data associated with urban renewal projects, including existing structures, utilities, and proposed changes, can be overwhelming and challenging to manage.
BIM Solution: BIM serves as a centralised platform for data management, storing all project information in a structured manner. This improves data accessibility and collaboration and ensures that all stakeholders are working with up-to-date and accurate information.
Also Read - Top 20 Urban Designer Firms in India & USA
Case Studies of BIM in Urban Projects
In the below case studies, BIM proved essential in overcoming challenges related to coordination, clash detection, visualisation, and sustainability analysis, ultimately contributing to the successful implementation of complex urban projects.
1. Garonne Eiffel Project, Bordeaux, France
The Garonne Eiffel initiative includes the restoration of a riverside vicinity in Bordeaux, France, adjacent to the Garonne River. This project transforms the former industrial area into a mixed-use development containing residential, commercial, and recreational spaces. The project faced several challenges such as managing complex urban infrastructure, coordinating multiple stakeholders, and ensuring compliance with environmental standards. The need for effective collaboration among architects, engineers, and construction teams was vital for the project's triumph.
BIM Implementation:
- BIM facilitated collaboration among architects, engineers, and construction teams.
- The 3D model made it easy to work together and identify potential issues early on.
- The digital model provided a realistic and detailed visualisation of the entire project.
- This visualisation helped stakeholders and the community better understand the proposed changes.
- BIM was used to develop detailed construction sequencing and phasing plans.
- It optimised the construction process, minimised disruptions, and enhanced overall project efficiency.
2. London Bridge Station Redevelopment, UK
The London Bridge Station redevelopment was a big project aimed at improving one of the busiest railway stations in London. The goal was to make the platforms larger, upgrade the infrastructure, and create new facilities for passengers. However, the complexity of the existing structures, tight construction schedules, and the need to minimise disruptions to the daily station operations are some of the challenges faced.
BIM Implementation:
- BIM played a key role in creating accurate models of existing station structures.
- BIM was used for clash detection to identify and resolve conflicts between new and existing elements.
- This significantly reduced the likelihood of on-site clashes during construction, saving time and resources.
- The 4D capabilities of BIM allowed the integration of time and scheduling information with the 3D model.
- This facilitated logistics planning, helping the construction team optimise the phasing of activities.
- BIM helped minimise disruptions to ongoing railway operations.
3. One Central Park, Sydney, Australia
One Central Park is a development in Sydney that includes residential buildings, shops, and a park. The goal was to make an environmentally friendly and visually appealing urban area. The project faced challenges in creating innovative green technologies, optimising energy efficiency, and designing a visually appealing space that blends well with the city.
BIM Implementation:
- BIM was crucial for modelling complex geometry and integrating intricate design features like green walls, ensuring construction accuracy and minimising errors.
- BIM was used to analyse and optimise the performance of green technologies, including energy efficiency, daylighting, and thermal performance, to achieve sustainability goals.
- BIM facilitated coordination among different disciplines involved in the project, such as architecture, landscape design, and environmental engineering.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration ensured seamless integration of all aspects of the project.
- The use of BIM helped in the accuracy of construction and reduced errors during the building process.
- BIM was instrumental in achieving sustainability goals by analysing and optimising the performance of green technologies.
Learning to Use BIM for Urban Designers
As BIM continues to reshape urban design, acquiring the necessary skills is not just an option but imperative. By embracing BIM, urban designers can enhance their capabilities, improve project efficiency, and contribute to the creation of sustainable and innovative urban spaces. Investing in BIM education and training is an essential step towards staying competitive in the market.
1. Understanding BIM Fundamentals
Urban designers need a solid understanding of BIM to fully grasp its fundamentals. BIM is a collaborative process that involves creating and managing digital representations of a building's physical and functional characteristics. Key BIM concepts include object-based modelling, data integration, and collaboration. BIM creates a 3D model of intelligent objects representing elements like walls, doors, and utilities, providing a comprehensive overview of a project's design, construction, and operational aspects. It also encourages real-time sharing and updating of project information among stakeholders.
2. BIM Courses and Training Programs for Urban Designers
Several specialised courses and training programs cater to urban designers aiming to integrate BIM into their skill set. Institutions, both online and traditional, offer comprehensive courses covering BIM basics, advanced applications, and industry-specific use cases. Examples include:
- Autodesk Certified BIM Training: Autodesk offers various BIM courses, including those specifically tailored for urban design applications using tools like AutoCAD and Revit.
- Online Courses: Ed-tech learning platforms like Novatr provide in-depth training on BIM methodologies and applications, emphasising real-world urban design scenarios. It also offers multiple capstone projects to test skills on, which helps build a portfolio as well.
- LinkedIn Learning and Udemy
Online platforms like LinkedIn Learning and Udemy offer a range of BIM courses, from beginner to advanced levels, allowing urban designers to learn at their own pace.
3. Application of BIM in Urban Design
BIM is a valuable tool for urban designers, enabling site analysis, visualisation, collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, and sustainable design. It allows for detailed 3D models of urban environments, facilitating better spatial relationships and enabling informed decision-making. BIM also supports sustainable urban design by integrating data on energy consumption, material usage, and environmental impact, promoting a more sustainable and efficient urban environment.
4. Strategies Implementation and Project Management
The successful implementation of BIM in urban design projects necessitates careful planning and execution. Key strategies include comprehensive team training, standardisation of BIM standards, gradual integration of BIM into workflows, and a centralised project management system for seamless communication among stakeholders. These strategies aim to maximise benefits, ensure consistency, and foster confidence among team members.
Conclusion
BIM is a transformative tool in urban design, offering a comprehensive digital representation of the built environment. It streamlines design and construction phases, facilitates ongoing management, and reduces errors. BIM fosters collaboration among architects, engineers, planners, and other stakeholders, ensuring accurate information and informed decision-making. It has the potential to revolutionise urban planning and development by enabling sustainable and resilient approaches.
By optimising resource utilisation, energy efficiency, and overall performance, BIM contributes to environmentally friendly cities and enhances quality of life. The future of BIM in urban design holds immense promise. As technology continues to advance, BIM will play a crucial role in shaping smarter, more sustainable, and resilient cities.
Embracing these innovations, as exemplified by the Novatr Architecture course, will be essential for professionals aiming to excel in the evolving field of urban design. Novatr's updated Architecture course now includes specialised modules catering to urban designers. The course is designed to equip professionals with the skills and knowledge needed to effectively leverage BIM urban design projects.


 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
-1.png)
.png)





.jpg)