Colonial Architecture: History, Elements, Characteristics & Examples

Table of Contents
Colonial architecture, prevalent from the 15th to mid-20th century, resulted from European colonialism in regions like the Americas, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. It features characteristic design elements such as large columns, arches, domes, and intricate ornamentation. Local materials and building practices led to the emergence of unique colonial style architecture across different regions. This blog post will discuss Colonial architecture, which combines Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque, Neoclassical, and Modernist styles and is characterized by hefty columns, arches, domes, and intricate ornamentation. Let us now explore a few examples to learn more about the colonial style architecture.
History Of Colonial Architecture
Colonial architecture originated during the age of European expansion, spanning from the 15th to the 20th century. As European powers such as the British, Spanish, French, and Dutch established colonies worldwide, they brought their architectural styles with them. However, these designs evolved to incorporate local materials, climate considerations, and indigenous influences. Spanish colonial architecture, for instance, integrated Moorish and Native American elements, while British colonial structures in India blended Gothic and Renaissance styles with traditional Indian motifs. This fusion created unique architectural identities across different regions.
Defining Elements of Colonial Architecture
Colonial architecture is distinguished by symmetry, grand facades, and a blend of European and local design elements. Buildings often feature evenly spaced windows, central doorways, and gabled or hipped roofs. Materials such as brick, stone, and stucco were commonly used, depending on regional availability. Many colonial structures include large columns, wide verandas, and decorative moldings. Spanish colonial buildings often have red-tiled roofs and stucco walls, while British colonial architecture incorporates high ceilings and large windows for ventilation. These defining features reflect both European sophistication and local adaptation.
Characteristics of Colonial Architecture
1. Symmetry and Proportion
Colonial buildings typically have balanced facades, with a central entrance flanked by evenly spaced windows. This reflects the European preference for order and harmony in design.
2. Local Adaptations
Architects and builders adjusted designs to suit regional climates and available materials. For example, Spanish colonial buildings in Mexico used adobe, while British colonial structures in India incorporated verandas and large windows for ventilation.
3. Ornate Details
Many colonial buildings include decorative moldings, intricate carvings, and classical elements such as columns, arches, and pediments, showcasing European influences.
4. Functional Design
Practical features like high ceilings for better air circulation, large porches for shade, and thick walls for insulation were incorporated, particularly in hot and humid regions.
Different styles of Colonial Architecture
1. Spanish Colonial Architecture
Found in Latin America, the southwestern U.S., and the Philippines, this style is characterised by red-tiled roofs, thick stucco walls, arched doorways, and enclosed courtyards. Influences from Moorish, Native American, and Baroque styles are evident in its design.
2. British Colonial Architecture
Common in North America, the Caribbean, and India, British colonial buildings feature symmetrical facades, classical columns, large windows, and gabled or hipped roofs. These structures often included verandas and raised foundations to suit tropical climates.
3. French Colonial Architecture
Prominent in Louisiana, the Caribbean, and parts of Africa, this style is known for its steeply pitched roofs, wraparound porches (galleries), wooden shutters, and raised floors to protect against flooding.
4. Dutch Colonial Architecture
Popular in early American settlements like New York and Pennsylvania, Dutch colonial buildings are recognisable by their gambrel roofs, brick construction, dormer windows, and large chimneys. Some also feature decorative brickwork and wooden shutters.
Advantage and Disadvantages Of Colonial Architecture
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Colonial architecture is known for its timeless elegance, symmetrical design, and intricate detailing, making it visually appealing. |
Ornate details, wooden structures, and large spaces require frequent upkeep, increasing maintenance expenses. |
|
Many colonial buildings were constructed using high-quality materials like stone, brick, and stucco, making them long-lasting. |
While adapted to local conditions, some features (like thick walls in humid areas) may not be ideal for all climates. |
|
High ceilings, large windows, and open layouts provide good ventilation and a comfortable living environment. |
Large plots of land are required, making colonial-style buildings less feasible in densely populated urban areas. |
Examples of Colonial Style Architecture
We often look at colonialism as an establishment of power and subjugation, but the introduction of the colonial milieu extends beyond dominion. The emergence of a timeless architectural style that sketched the urban fabric of many countries is a prominent mix of the history and context of the colonized country. Some prominent colonial styles include Portuguese, British, French, Spanish, Italian, and Dutch. Here are a few examples highlighting Colonial Architecture around the world.
1. Victoria Memorial, Kolkata, India (1906-1921)
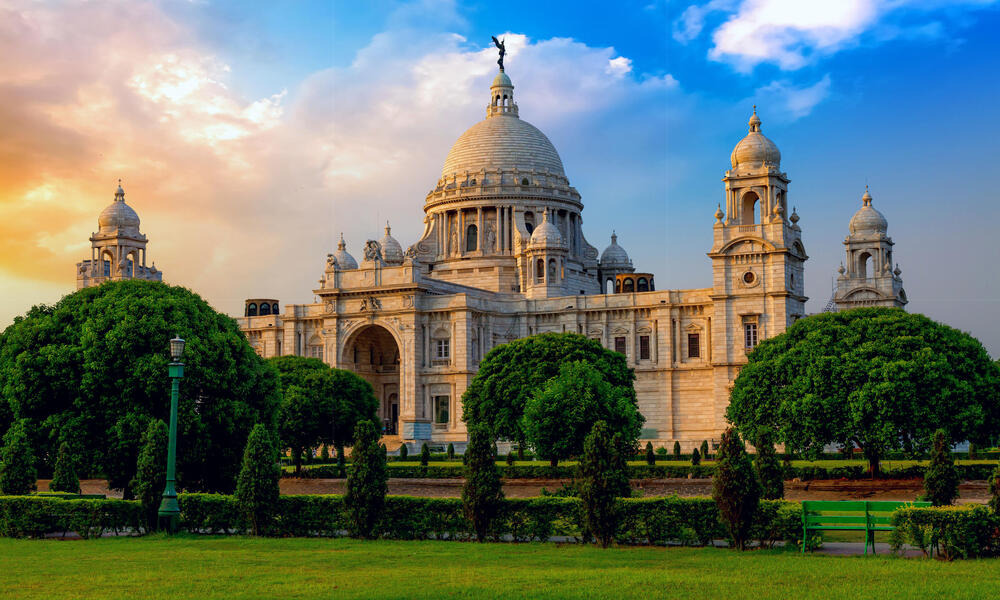

Design Features
- The Victoria Memorial blends Indo-Islamic, British, and Mughal design popular during the era of colonial architecture in India.
- The memorial features a tall central dome, adding to its grandeur.
- Elaborate carvings, sculptures, and ornamental motifs showcase exquisite craftsmanship.
- Inside, the museum displays a vast collection of artifacts, paintings, and exhibits from colonial architecture in India.
- The memorial's central hall features high ceilings, elegant columns, and artistic displays commemorating Queen Victoria and the colonial architecture period.
Victoria Memorial is an iconic colonial architectural marvel located in Kolkata, India. Built during the British colonial period, it stands as a symbol of the grandeur and influence of the British Empire in India. The memorial showcases a fusion of architectural styles, blending Indo-Islamic, British, and Mughal design elements.
2. The San Francisco de Asis Church, New Mexico, USA (1772-1816)
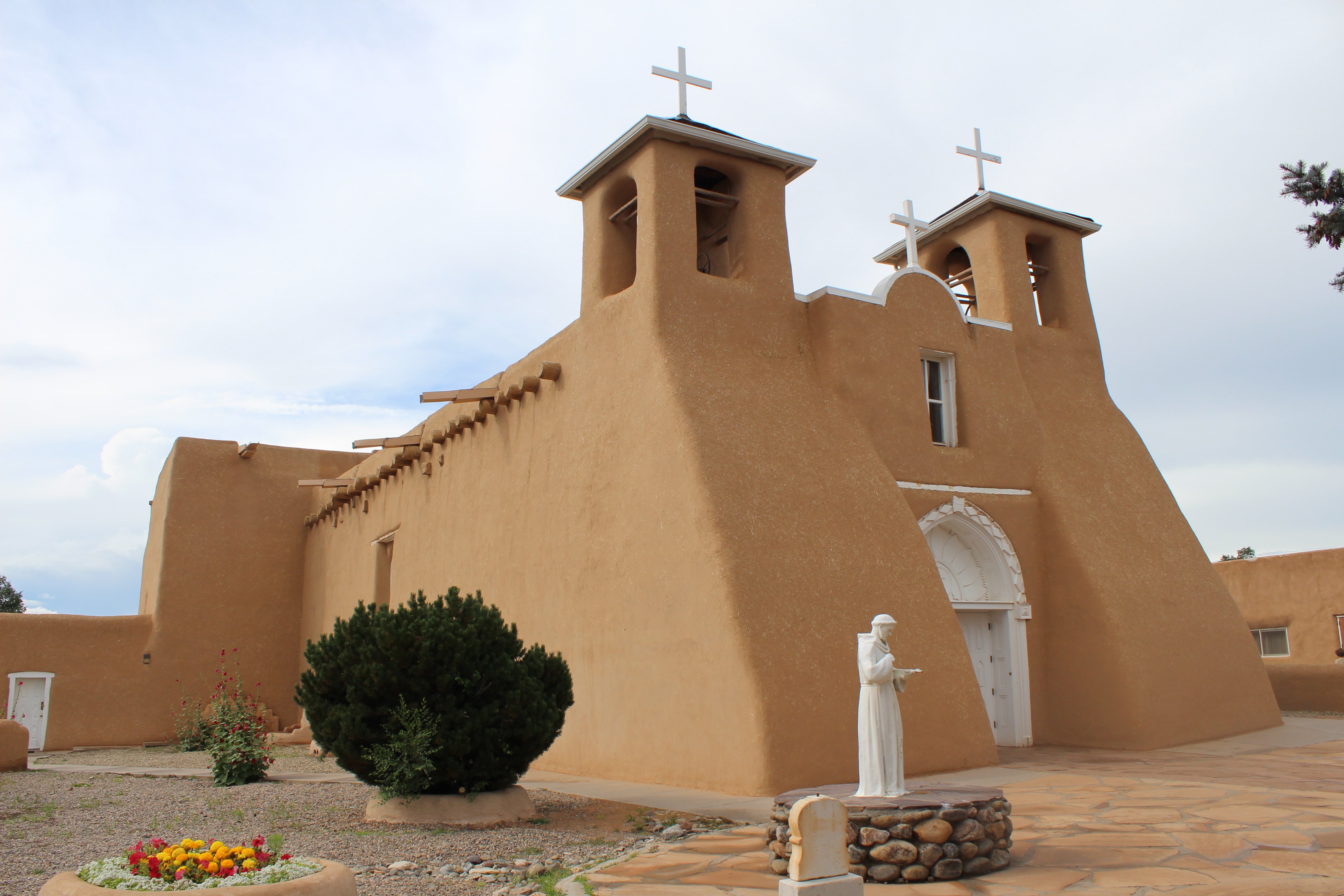

Design Features
- The church displays adobe architecture with smooth, rounded walls, commonly used in the colonial era.
- It has a traditional octagonal layout, emphasizing the cross-shaped floor plan and religious symbolism.
- The front facade features a simple entrance portal with a rounded arch and decorative details.
- The altar is elevated and ornately decorated with carved wooden altars and religious artwork.
- It also includes a courtyard for religious gatherings and festivals.
- It is a mix of Spanish colonial architecture and Native American architectural influences, reflecting the region's cultural heritage.
The San Francisco de Asis Church in Ranchos de Taos, New Mexico, USA, was constructed by the Spanish settlers between 1772 and 1816, serving as a place of worship for the local community of indigenous peoples and Spanish colonizers. Notably, the church is a prominent illustration of Adobe-style architecture type of dried mud brick in the southwestern United States.
Also Read: Passive Strategies for Building Design in Tropical Climates: A Comprehensive Guide
3. The Governor's Palace, Williamsburg, Virginia, USA (1706-1722)
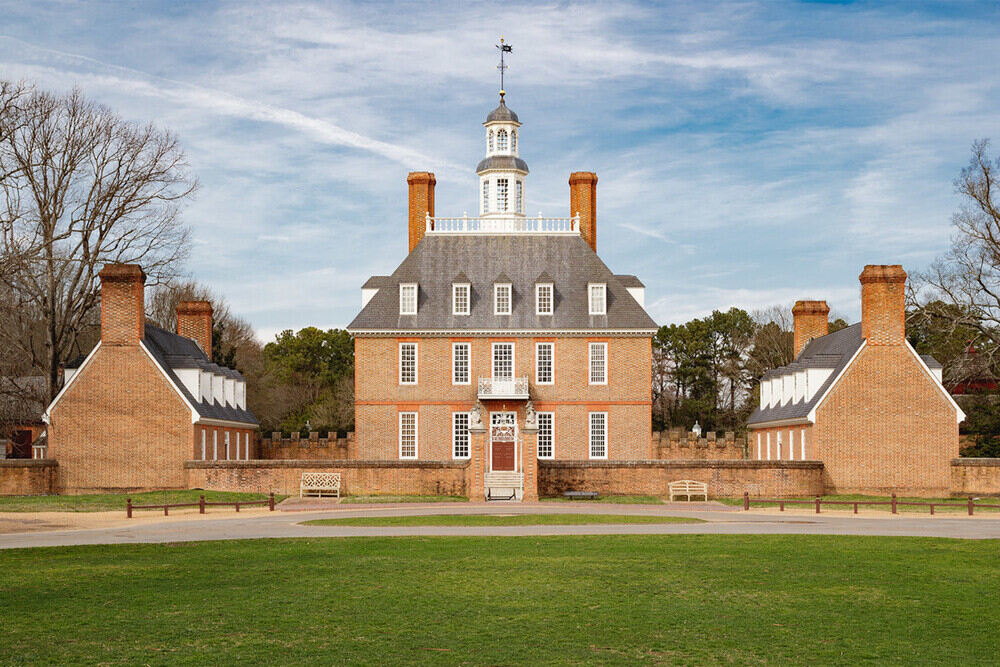

Design Features
- The Palace displays Georgian architectural colonial style house, which reflects British design aesthetics.
- Its symmetrical exterior design includes a central entrance surrounded by windows and chimneys each equally spaced.
- The imposing columns, mouldings, pillars, and ornate carvings adorn the grand façade.
- High ceilings define plasterwork, intricate woodwork, and decorative paneling adorn the spacious interior.
- The formal gardens surrounding the palace have been carefully planned with geometric flower beds.
The Governor's Palace is a historic and colonial building located in Colonial Williamsburg, Virginia, USA, built-in 1722 by the colonial governor Francis Nicholson and served as the residence for the royal governors of Virginia until the American Revolution. The palace was designed as one of the largest buildings in colonial architecture in America. Presently, it is being accommodated as a museum within the Colonial Williamsburg Historic Area, attracting many visitors and providing a glimpse into Virginia's colonial architecture past.
4. The Cathedral of Santa Maria la Menor, Dominican Republic (1514-1541)
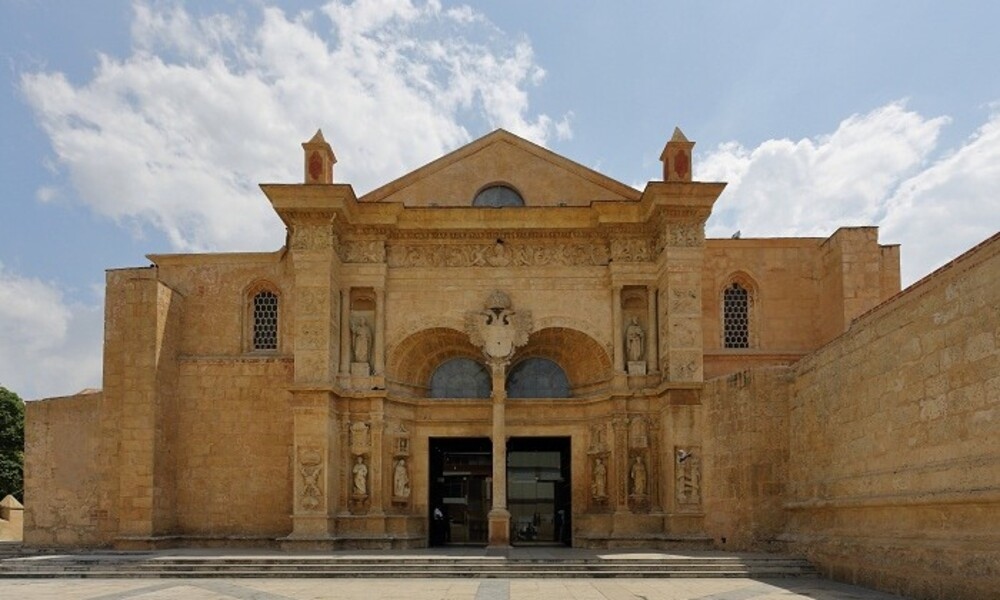

Design Features
- Gothic and Renaissance architectural styles were influenced by the Spanish colonial architecture period.
- Intricate stonework and ornate detailing on the exterior showcase craftsmanship.
- Chapels are dedicated to saints with unique designs and decorations.
- Colourful stained glass windows depict biblical scenes and religious symbolism.
- Elaborate altar with carvings and religious iconography.
- Possible central dome or domed ceiling for architectural grandeur.
- Reflects the colonial era's influence on religious architecture in the Dominican Republic.
The Cathedral of Santa Maria la Menor in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic, is one of the oldest cathedrals in the world, built between 1514 and 1541 by Spanish colonists and serving as the New World's first cathedral. It was the first cathedral constructed outside of Europe.
The cathedral was named a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1990.
5. The St. Paul's Cathedral, London, UK (1675-1708)
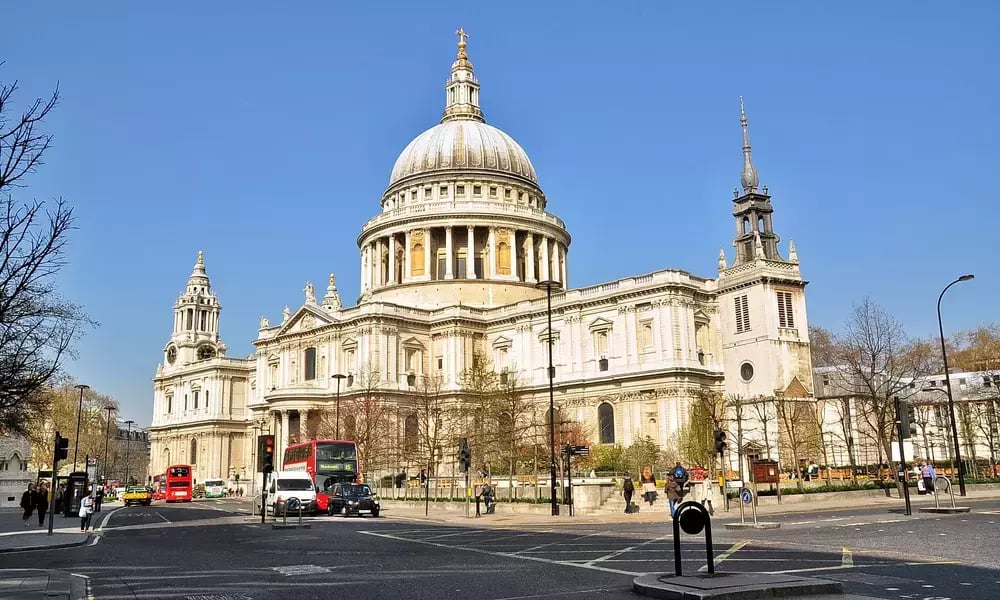

Design Features
- English Baroque architectural style with grand proportions and elaborate ornamentation.
- Renaissance and Italian architecture inspired the majestic dome.
- It consists of classical components like pediments, pilasters, and columns.
- Its colonial interior design features high ceilings, beautiful arches, and decorative touches.
- It is a Famous Whispering Gallery with unique acoustic properties.
- A monument honouring London's Great Fire and the city's reconstruction.
St. Paul's Cathedral is located in the City of London, United Kingdom, on Ludgate Hill. It was built between 1675 and 1710 after the Great Fire of London in 1666 destroyed the previous cathedral. The cathedral was designed by Sir Christopher Wren, an English architect who was also responsible for many other notable colonial buildings in London.
6. The City Hall, Cape Town, South Africa (1905-1908)
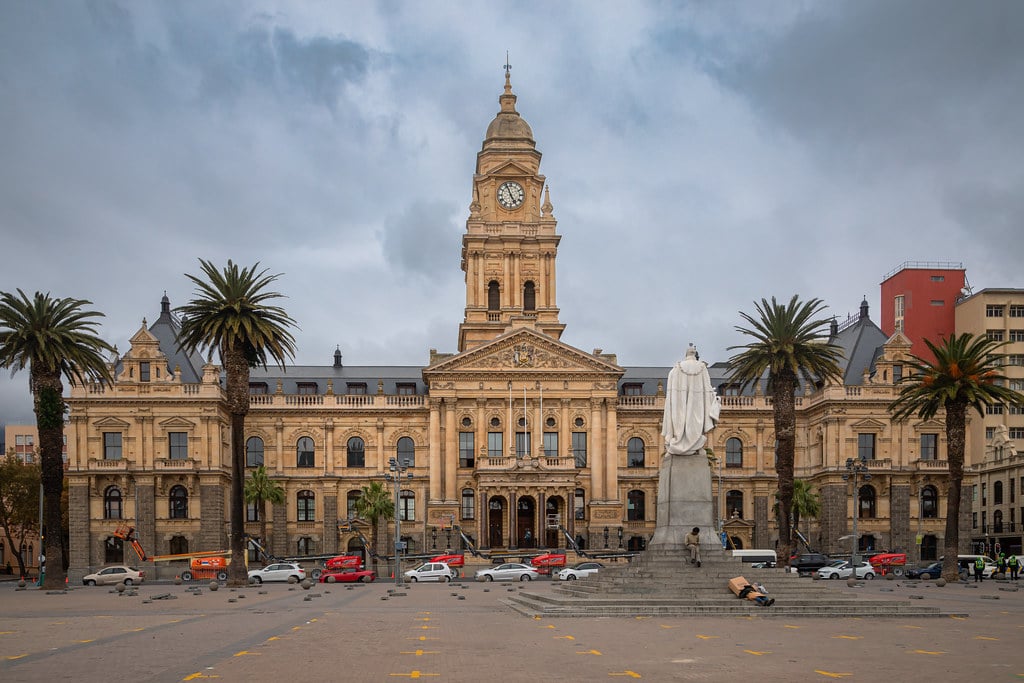

Design Features
- Elaborate facade with tracery, cornices, and carvings.
- Grand entrance with columns, portico, or arched doorway.
- Large windows with intricate tracery or decorative accents.
- Central atrium or hall with high ceilings and ornamental columns.
- It houses historical relics, sculptures, or artwork reflecting colonial style architecture and local history.
The City Hall in Cape Town, South Africa, is a notable neoclassical building built in the early 20th century. It has played a significant role in the country's history, hosting political and cultural events, including the inauguration of Nelson Mandela as the first democratically elected president in 1994. The colonial building remains a popular tourist destination and is still utilized as the seat of the government for the City of Cape Town.
7. The Palacio de los Capitanes Generales, Cuba (1776-1791)
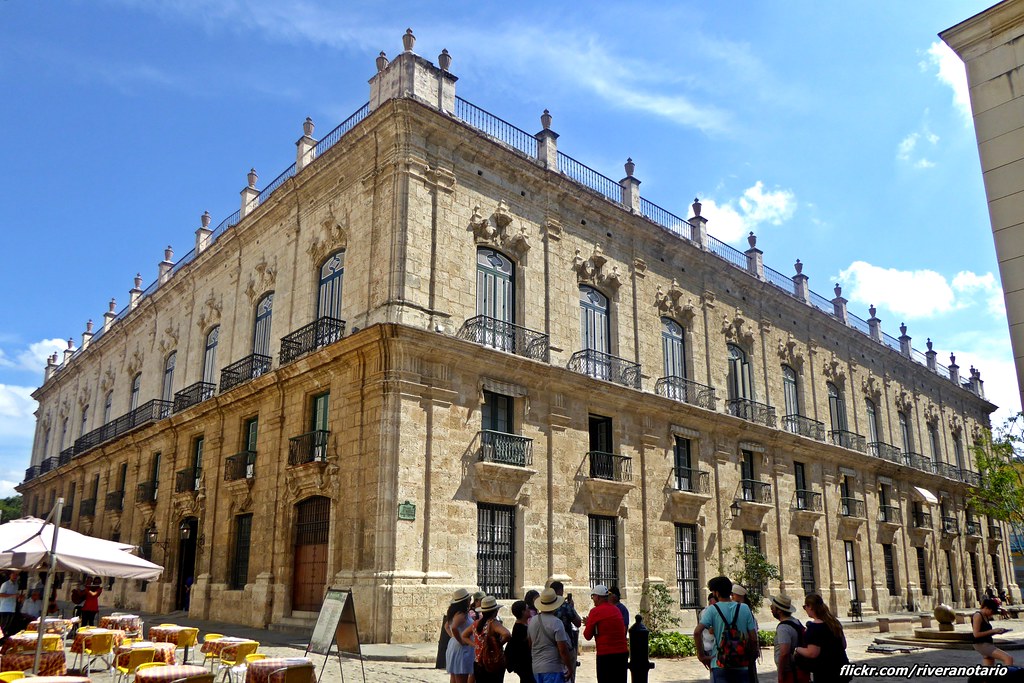

Design Features
- Spanish colonial architectural styles combined Baroque and neoclassical design.
- Grand facade with ornate details, balconies, pilasters, and intricate stonework.
- Inner courtyard for gathering, ventilation, and natural light.
- Delicately crafted wooden balconies ("rejas") showcasing elegance.
- Former extensive gardens with lush vegetation, fountains, and pathways.
- Arched doorways add grandeur and an inviting entrance.
- Colonial-era rooms and halls with decorative ceilings, elegant furnishings, and historic artifacts.
Cuba's Old Havana is home to the historic Palacio de los Capitanes Generales. During the colonial style architecture era, it was constructed between 1776 and 1791 and used to house the Spanish governor-captains of the island. The design blends Baroque, Neoclassical, and Cuban architectural styles. It has been converted into a museum, at present, showcasing the history and culture of Havana, with exhibitions on colonial architecture history, decorative arts, and urban development, and it is also home to the City Museum.
8. The Wat Phra Kaew, Thailand (1782-1784)
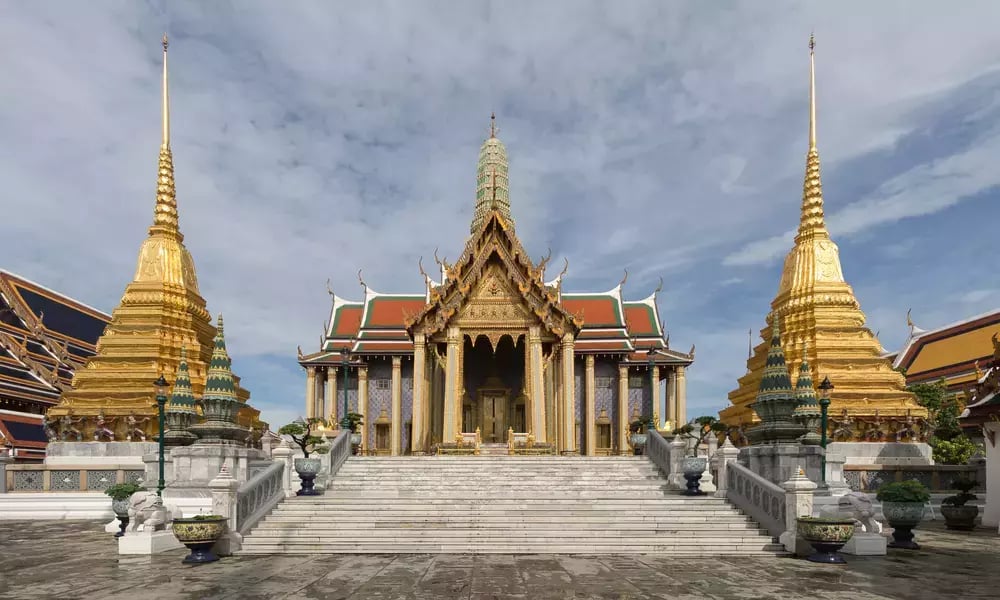

Design Features
- It is a significant Buddhist temple located within the grounds of the Grand Palace in Bangkok, Thailand.
- The main building is highly ornate, housing the sacred Emerald Buddha statue.
- Multi-tiered roofs is a distinctive feature.
- Intricate mural paintings on the walls depict scenes from Buddhist mythology and Thai folklore.
- Giant guardian statues called yakshas protect the temple entrances and corners.
- Murals, sculptures, and artifacts are displayed in covered cloisters and galleries.
- Prangs are tower-like buildings with intricate designs and spires, inspired by Khmer and Ayutthayan architectural styles.
The temple and Grand Palace were built by King Rama I, the founder of the Chakri dynasty, and have been renovated and expanded by subsequent monarchs. They are important cultural symbols of Thailand and popular tourist destinations.The Temple of the Emerald Buddha, also known as Wat Phra Kaew, is located within the grounds of the Grand Palace in Bangkok's historic district, Thailand.
9. The CASA Rosada, Argentina (1873-1898)
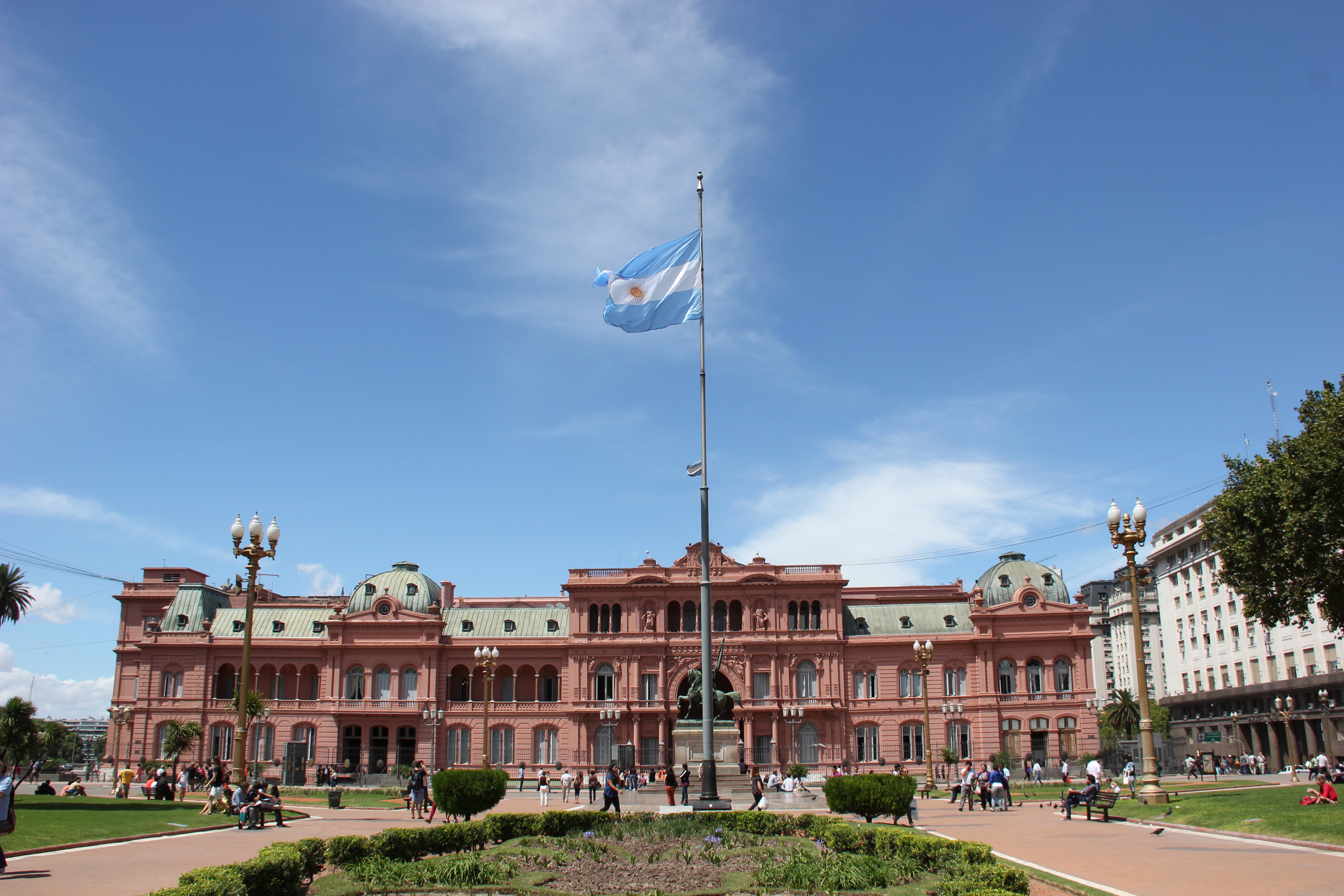

Design Features
- Neoclassical architecture with symmetrical designs, decorative columns, and grand facades.
- Iconic pink-coloured facade achieved with a mixture of lime and bovine blood.
- Italian architectural influences with ornate details and decorative elements.
- The prominent entrance balcony, known as the "Balcony of the Argentine People," was used for speeches.
- Courtyards and patios provide open spaces for gatherings.
- Interior rooms and halls for governmental activities, showcasing architectural details and artifacts.
The palace's standout features are its Neoclassical design, central tower, and ornate balconies. It also houses several murals, sculptures, and other artworks that depict significant moments in Argentine history. It was built between 1873 and 1898 and has served as the Argentine government's seat ever since.
10. The Fort Jesus, Kenya (1593-1596)
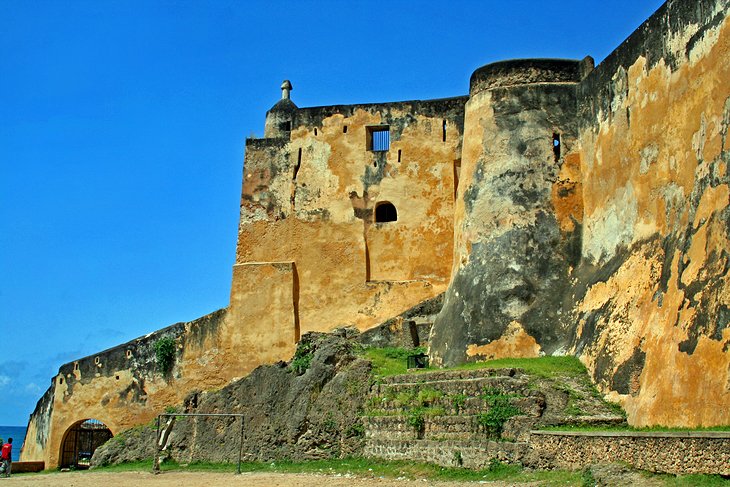

Design Features
- Star-shaped design with five main bastions for improved defence and visibility.
- Thick coral stone walls, up to 18 meters of protection against attacks and cannon fire.
- Water moat surrounding the fort, connected to the sea for direct supply access.
- Living quarters and storage rooms for garrison and supplies.
- Decorative elements like intricate stonework, arches, and ornamental details.
- Doubles as a museum with exhibits showcasing colonial-era artifacts and regional history.
Fort Jesus is a historical fort in Mombasa, Kenya, was constructed by the Portuguese between 1593 and 1596 to protect their interests and control the Indian Ocean trade routes. Its location at the entrance of the Old Port of Mombasa made it an impregnable fortress. As one of the best-preserved examples of Portuguese military architecture, it is now a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Also Read: Passive Design Strategies for Composite Climate
In conclusion
Colonial architecture is a testament to the historical and cultural influences of European colonialism in regions around the world. It emerged as a fusion of various architectural styles, incorporating elements from Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque, Neoclassical, and Modernist movements. The architectural landmarks discussed in this blog post showcase the diversity and grandeur of colonial architecture, each reflecting its location's unique cultural and historical context. These architectural landmarks serve as historical and cultural icons and attract millions of visitors, offering glimpses into the colonial past of different nations. They stand as reminders of colonialism, provoking contemplation and an understanding of the historical context in which they were built.
Do you aspire to create architectural marvels such as those featured in this blog? If so, look into Novatr's Master Computational Design Course. The computational design creates complicated patterns and decorative features that combine traditional beauty with modern efficiency and precision. Discover industrial practices, advanced tools, and computational theory to visualise and easily design iconic structures.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
-1.png)

.png)