Top 10 Materials to Enhance Building Facade Performance

Table of Contents
The choice of building materials is critical for a building's performance. It helps determine and influences various building features including energy efficiency, durability, indoor air quality, and aesthetics. Architects, builders, and designers must consider material properties to optimize performance. Green building guidelines and rating systems serve valuable guidance for selecting environmentally-friendly materials for sustainable buildings.
Post the global pandemic outbreak, the effect of materials on a building's performance has come to people's attention more recently. The durability, indoor air quality, acoustic performance, aesthetics, and environmental impact of a building can all be significantly impacted by the choice of building materials. Several green building guidelines and rating systems have been developed for architects, builders, and designers to choose environmentally friendly materials that support environmentally friendly construction.
Impact of Materials on Buildings' Performance
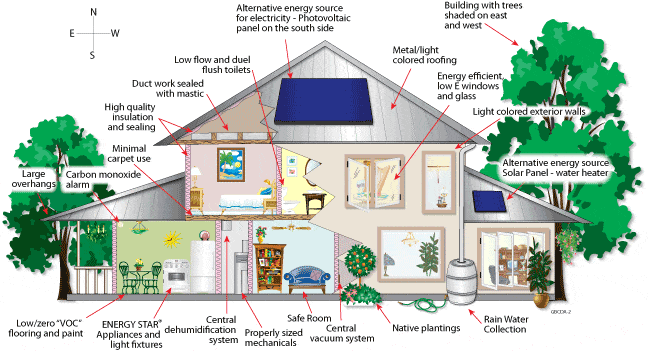
The choice of materials in construction plays a crucial role in determining a building's performance and functionality. Material selection can lead to energy-efficient, durable, healthy, and aesthetically pleasing structures while minimizing environmental impact. They also affect the indoor environmental quality (IEQ), influencing the health of those who occupy the building.
1. Energy Efficiency: The insulation, windows, and roofing materials used in the facade of a building may affect how much energy the structure uses. For instance, installing high-performance design windows with low-E coatings can lower both summer and winter heat gain and loss, thus reducing the need for heating and cooling.
2. Durability: The maintenance costs and longevity of a building can be affected by the durability of the building materials. Mould development and damage caused by water can be prevented with the help of materials that are resistant to weathering and moisture. On the other hand, materials that are prone to deterioration or corrosion may eventually cause structural problems.
3. Indoor Air Quality: The materials used in a building's interior, such as flooring, wall coverings, and paint, can impact indoor air quality. Certain materials can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to poor indoor air quality and health issues. Choosing materials with low or no VOCs can help improve indoor air quality.
Also Read: Introduction to Building Energy Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide (2023)
4. Acoustic Performance: The acoustic performance of a building can be affected by the materials used in its building. For instance, using materials with high sound absorption rates may reduce the amount of noise that is transmitted between rooms, whereas using materials with high noise transmission rates can facilitate easier noise transmission.
5. Aesthetics: The facade of a building structure can affect both its aesthetic appeal and overall value. Materials that are aesthetically pleasing and enhance the building's facade design can make it more visually appealing and profitable.
6. Environmental Impact: The surroundings may be impacted by construction materials, including energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and the depletion of the earth's resources. Utilizing green building materials, like recycled or renewable ones, can lessen a structure's negative environmental effects.

Green Building Guidelines

Architects, builders, and designers may select building materials that have a favourable effect on the energy efficiency of a structure by following one of the many green building guidelines and evaluation methods available.
1. LEED: A well-known environmentally friendly construction certification program is the LEED rating system (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). For the building, and functioning of sustainable buildings, LEED offers norms and recommendations. One of the primary groups in the LEED rating system, materials, and resources, offers suggestions for choosing eco-friendly materials, cutting waste, and maximizing resource use.
2. WELL Building Standard: The WELL Building Standard is a certification program that mainly focuses on building occupant health and wellness. It provides guidelines for selecting materials that contribute to a healthy indoor environment, such as materials with low or no VOCs and those that are easy to clean.
3. Living Building Challenge: Buildings must adhere to strict criteria to earn environmental sustainability and efficiency to receive the Living Building Challenge certification. It offers guidelines for choosing environmentally friendly, regionally produced, and ethically harvested materials.
4. Cradle to Cradle: Cradle to Cradle is a sustainable facade design framework that emphasizes the use of materials that can be safely and effectively recycled or biodegraded. It provides guidelines for selecting materials that positively impact the environment throughout their lifecycle.
5. Green Globes: Green Globes is a green building certification program that provides guidelines for sustainable building facade design and operation. Materials and resources are the key categories in the Green Globes rating system. It gives guidelines for selecting environmentally friendly, low-emitting, and energy-efficient materials.
List of materials for building facades
Facades are essential for building design, functionality, and performance. Common materials include insulated glass, aluminum composite panels, terracotta, fiber cement, zinc, stone, and ceramic tiles. Each material offers benefits like energy efficiency, thermal performance, durability, weather resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these materials helps architects and builders create visually appealing, functional, and sustainable building facades.

1. Insulated Glass
A building's efficiency can be enhanced with insulating glass, also referred to as double- or triple-glazed glass, resulting in better energy usage, acoustic performance, and indoor comfort. This building material consists of two or more glass panes spaced apart by an insulating gas or air spacer. The glass panes' low-emissivity (low-E) coating reduces heat transfer, increasing energy efficiency. Insulated glass also lessens noise transmission and aids in maintaining a cozy interior temperature by minimizing heat gain and loss, which lowers heating and cooling expenses while enhancing occupant comfort.
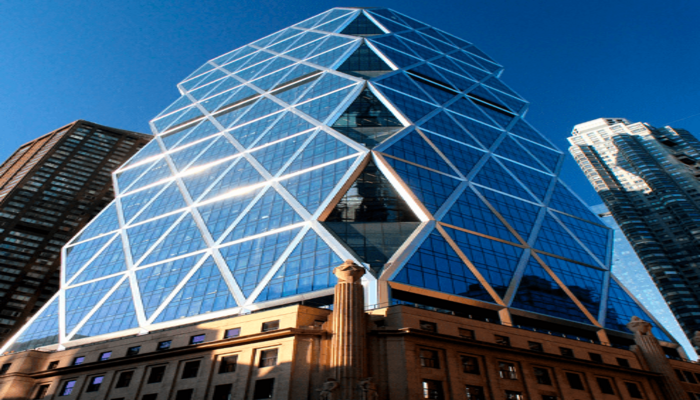

All of the windows of the Hearst Tower in New York City are double-glazed insulated glass, and the building facade is supported by a diagrid structural system made of glass and steel. Insulated glass improves the building's energy efficiency, reduces noise transmission, and keeps people comfortable inside. The structure's thermal performance is additionally improved by the low-E coating on the glass, which is designed to reduce solar heat gain.
2. Aluminum Composite Panels
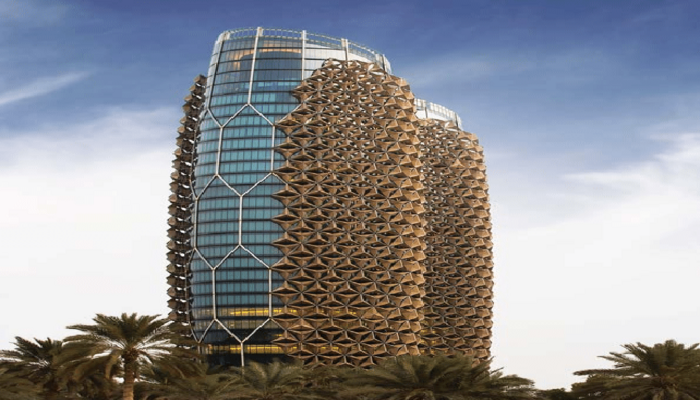

Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP) enhance a building facade's energy efficiency, sustainability, and aesthetics performance. Manufacturers bond two aluminum sheets to a core material that can be customized with various textures, colours, and finishes. ACP withstands weathering, corrosion, and impact and reflects sunlight, which reduces cooling costs. These properties make ACP a popular choice for a wide range of construction applications.
The Al Bahr Towers in Abu Dhabi, UAE feature a dynamic, geometric pattern created using aluminum composite panels. These panels provide a durable and weather-resistant finish while minimizing heat transfer through the building facade, contributing to the building's energy efficiency. The reflective finish of the panels also creates a comfortable indoor environment by reducing solar heat gain. Additionally, ACP also reduces the building's overall weight, lowering construction costs and improving structural performance.
Also Read: Energy-Efficient Buildings: The First Step in Design for a Better Future
3. Terracotta
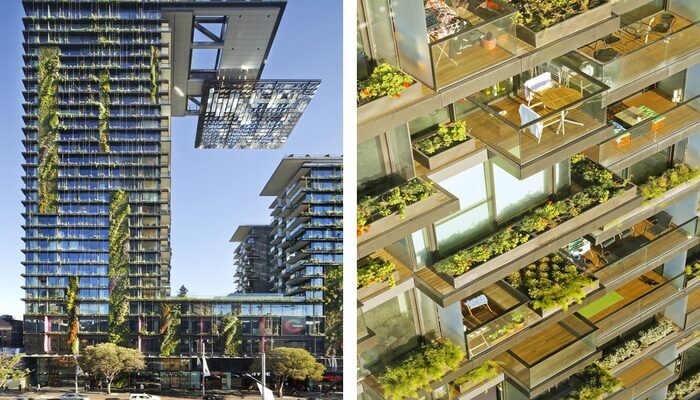

Terracotta, a sustainable and durable building material, can enhance a building facade's performance. Manufacturers mould natural clay into various shapes and fire it at high temperatures, which gives an attractive finish. This versatile material is available in different colours and textures, making it customizable. It resists weathering, corrosion, and impact, making it a cost-effective choice. Terracotta also provides insulation, and thermal mass, contributing to a building's energy efficiency.
The One Central Park building in Sydney, Australia features a building facade system with vertical gardens and terracotta sunscreens that provide shade and reduce solar heat gain. Terracotta sunscreens contribute to the building's energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer through the facade. Using terracotta helped to create an attractive and sustainable building envelope that blends in with the natural surroundings of the building's park setting.
4. Fibre Cement

Fibre cement is a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibres and is used as a long-lasting, fire-resistant, and low-maintenance building material. It offers flexibility in customized design with a variety of colours and shapes. It is resistant to rust, impact, weathering, and pests. High-fire-risk areas are secured to use because of their resistance to fire.
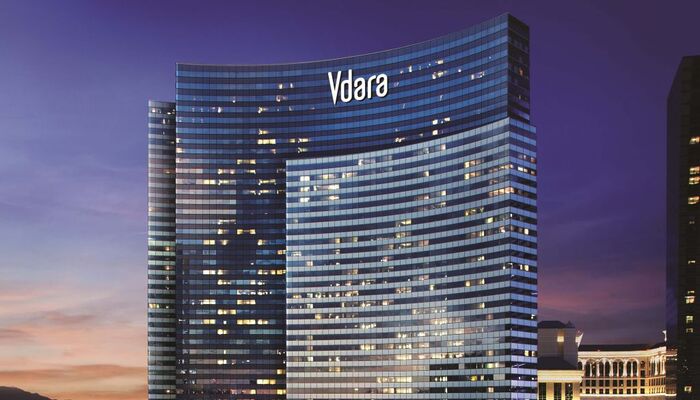
The Vdara Hotel & Spa in Las Vegas, USA, features a sleek and modern building facade system made of fibre cement panels, available in a range of colours and textures. It creates an attractive and low-maintenance building envelope, while the fire-resistant properties of fibre cement reduce the risk of fire spreading to adjacent buildings, ensuring the safety of occupants.

5. Zinc

Zinc is a sustainable, durable, and corrosion-resistant building material that enhances a building facade's performance. It is customized in different finishes to meet specific design requirements and is long-lasting, low-maintenance, and energy-efficient. Zinc is not only attractive but also sustainable and energy-efficient due to its 100% recyclability, making it a desirable building material.
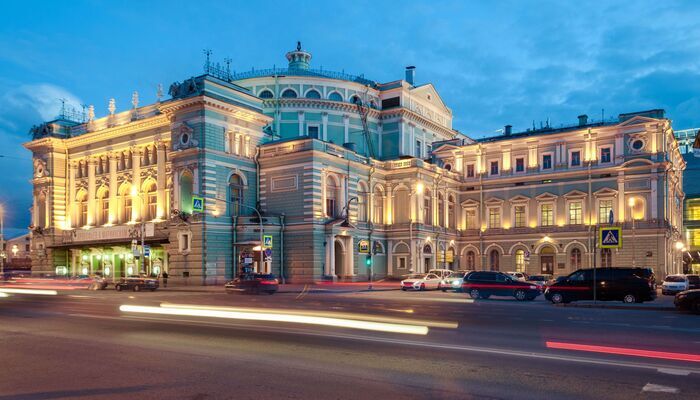
The New Mariinsky Theatre in St. Petersburg, Russia, has a distinctive and exquisite zinc-panelled building envelope. The panels were chosen for their durability, sustainability, and aesthetically pleasing appearance. The reflecting properties of zinc restrict heat from the sun gain and enhance the energy performance of the structure.
6. Stone
Stone is a naturally occurring material, used for various building applications, including cladding, panels, and tiles. It possesses unique characteristics like durability, natural beauty, and thermal performance. It resists weathering, corrosion, and impact, making it a cost-effective option for building facades. The natural beauty of stone enhances a building's visual appeal, while its excellent thermal performance regulates indoor temperatures and reduces the energy consumption required for heating and cooling.

The limestone-panelled building envelope of the Kimbell Art Museum in Texas is long-lasting, and its thermal performance improves the building's energy efficiency by lowering the amount of energy required for cooling and heating.
7. Ceramic Tiles

Ceramic tiles offer durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal, making them ideal for building facades. They are made from natural materials like clay and resist weathering, impact, and wear and tear, requiring minimal maintenance over their long lifespan. Ceramic tiles are available in various colours, sizes, and textures, allowing for unique patterns and design applications. Their beautiful and elegant appearance can be customized to match specific design requirements, creating a modern look for a building's exterior.
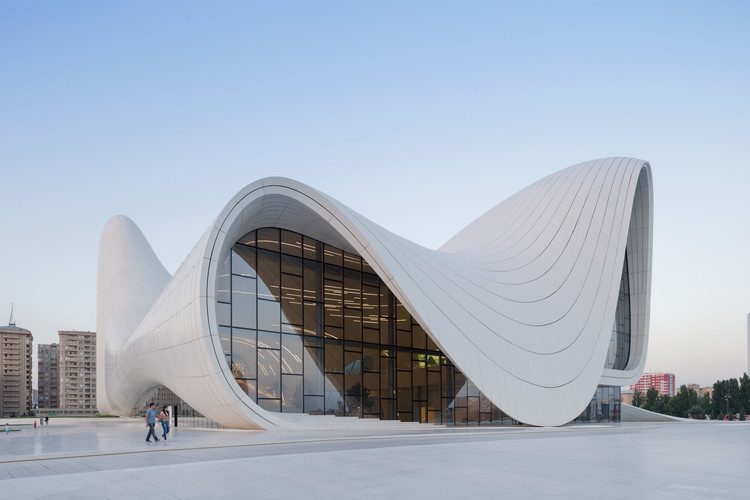
The Heydar Aliyev Centre in Baku, Azerbaijan, has a sleek and contemporary white ceramic tile building façade. The ceramic tiles are chosen because of their durability, adaptability, and aesthetic value. The water-resistant features of these tiles preserve the structure from humidity and moisture, which is essential in the humid climate of the region.
Read more: High Performance Building Design With Computational Design: Everything You Need to Know
8. Brick
Brick is a time-honoured material known for its durability, thermal performance, and aesthetic versatility. Facades made using bricks offer excellent thermal mass properties, helping to regulate indoor temperatures and reduce the reliance on mechanical heating and cooling systems. Additionally, brick is highly durable and low-maintenance, providing long-term structural integrity and resilience against weathering and environmental factors. Moreover, the modular nature of brick construction allows for efficient installation and repair, further optimizing building performance over time.
9. Metal Mesh

Metal mesh is a versatile material that combines aesthetic appeal with functional benefits such as solar shading, natural ventilation, and daylighting control. It offers excellent airflow and light diffusion properties, promoting natural ventilation and daylight penetration while minimizing glare and heat gain. Additionally, the lightweight nature of metal mesh reduces structural loads and material consumption, contributing to overall energy efficiency and sustainability. An exemplary use of metal mesh can be observed in the Eden Project in Cornwall, England. Designed by architects Grimshaw, the project features a series of large biomes covered with ETFE (ethylene tetrafluoroethylene) cushions supported by a steel framework and surrounded by a striking outer cladding of hexagonal metal mesh panels.
10. Glass Reinforced Concrete

Glass reinforced concrete (GRC) combines the strength and durability of concrete with the flexibility and lightweight properties of glass fibers, offering architects a versatile material for creating innovative facade designs. It provide architects with the freedom to realize complex geometries and sculptural forms while maintaining structural integrity and weather resistance. The Yas Viceroy Abu Dhabi Hotel, designed by Asymptote Architecture, exemplifies the use of GRC in contemporary architecture. The hotel's futuristic form is clad in a dynamic double-curved gridshell structure made from GRC panels, creating a visually striking facade that reflects the surrounding landscape and captures the essence of modernity and luxury.
In conclusion
The materials used in the facade of a building can substantially impact its performance and overall quality. Factors such as energy efficiency, durability, indoor air quality, acoustic performance, and aesthetics are all influenced by the choice of materials. Architects, builders, and designers should carefully consider the characteristics and properties of different materials to optimize building performance in these areas. Furthermore, the availability of green guidelines and rating systems provides valuable assistance in selecting environmentally-friendly materials that contribute to a sustainable and eco-friendly built environment. By incorporating these guidelines into the material selection process, professionals in the construction industry can ensure that buildings are functional and visually appealing, energy-efficient, durable, and environmentally responsible. Ultimately, the thoughtful choice of materials can lead to buildings that enhance the well-being of occupants, minimize environmental impact, and contribute positively to the communities they serve.
With the resources accessible today, it is simple to begin studying topics that interest you. Discover comprehensive online designing courses with Novatr if you need help breaking out of your comfort zone! Visit our Resources page to learn more about current architectural and design trends. Novatr's Master Computational Course will teach you how to create sustainably utilizing digital design technology.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!
-1.png)

.png)