Top 10 Examples of Modular & Prefabricated Home Architecture (2025)
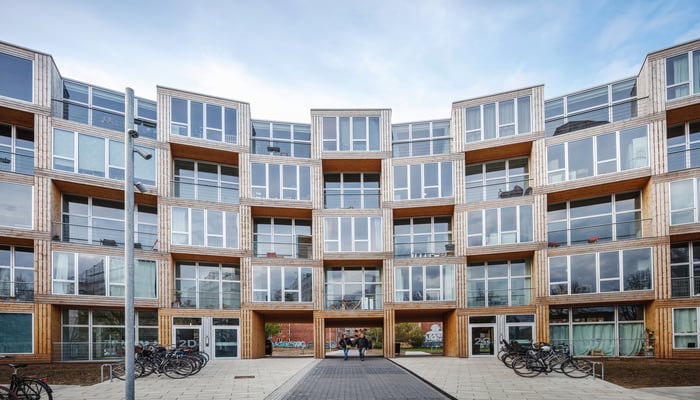

Table of Contents
Imagine a world where homes are built with precision and speed, where customisation knows no bounds, and where sustainability takes centre stage. As we all know, innovation is key to addressing the evolving needs of society. One such innovation that has been gaining traction in recent years is modular and prefabricated houses or home architecture. This construction method offers a plethora of benefits, from cost savings and sustainability to flexibility and speed. In this blog, we will learn about the meaning of prefabricated and modular structures, their advantages, and some projects that incorporate their concept.
What is Modular and Prefabricated Home Architecture?
Modular and prefabricated home architecture refers to a construction method or approach where building components are constructed and manufactured off-site in a factory-controlled environment, and later transported to the real construction site for assembly.
In this method, the structure of the home is divided into multiple modules and sections, which are prefabricated in a factory setting. These modules can range from entire rooms to smaller components like walls, windows, roofs etc. Modular wooden houses and prefabricated structures are similar in that they are both built off-site in a factory or manufacturing facility.
However, there is a difference between the two in terms of their construction and transportation.
Modular homes are built in modules or sections that are transported to the building site and assembled on a permanent foundation. These modules are typically built to meet state or local building codes, and the finished home looks like a traditional site-built home. On the other hand, prefabricated structure can refer to a variety of building types, including modular homes, but they also include other types of buildings that are prefabricated off-site, such as panelised homes, mobile homes, and even commercial buildings like office spaces or warehouses. These structures can be built using different materials, and construction methods, and they may offer varying levels of customisation.
The emergence of prefabricated and modular homes architecture has changed the way buildings are constructed today. You can now build prefabricated spaces in sections and then assemble them quickly on the actual site to reduce the turnaround time. They are leading the charge in the architectural revolution, reshaping the way we think about the spaces we live in.
Advantages of Prefabricated and Modular Homes
As discussed above, prefabricated structures are types of housing that are built off-site in a factory or manufacturing facility and then transported to the final location for assembly. Modular prefabricated homes, on the other hand, are a type of prefabricated homes that are built at least 70% off-site. Both prefabricated homes offer several advantages over traditional site-built homes, including cost savings, faster construction times, and increased design flexibility.
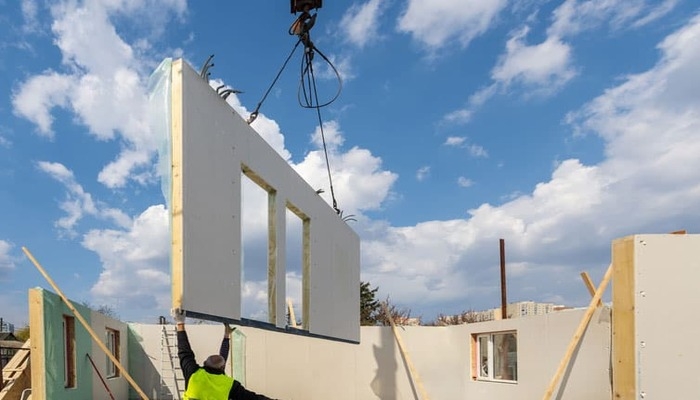

These structures are types of housing that are built off-site in a factory or manufacturing facility and then transported to the final location for assembly. Prefabricated homes offer several advantages over traditional site-built homes, including cost savings, faster construction times, and increased design flexibility.
Cost-effective: Prefabricated and modular homes are often more cost-effective compared to traditional site-built homes. The controlled factory environment allows for the efficient use of materials and reduced waste.
Faster Construction: Since prefabricated and modular homes are built in a factory setting, the construction process is not affected by weather conditions. This allows for faster construction times, and homeowners can move into their new homes sooner.
Design Flexibility: Modular homes, in particular, offer a high level of design flexibility. They can be customised to suit specific needs and preferences, allowing homeowners to choose from a wide range of floor plans, finishes, and fixtures.
Quality Control: Construction in a factory environment allows for better quality control as the manufacturing process is closely monitored. The use of standardised techniques and inspections helps ensure that the homes meet high-quality standards.
Energy-efficient: Prefabricated and modular homes often incorporate energy-efficient features and materials, such as improved insulation, energy-efficient windows, and energy-saving appliances. This can result in lower utility costs and a reduced environmental footprint.
Portability: In some cases, prefabricated and modular homes can be disassembled and moved to a different location if needed. This makes them suitable for temporary housing or situations where mobility is required.
Read more: What is Modular Architecture, Its Advantages, And 10 Examples
Examples of Modular/Prefabricated Homes
Prefabricated homes, often referred to as prefab homes, have become increasingly popular over the last few years. They represent a revolutionary approach to residential constructions and are slowly but steadily becoming a compelling solution for meeting diverse housing needs. Let us learn about some examples of prefabricated and modular homes that showcase a diverse range of designs and styles.
1. VDC (Vale De Cambra) by SUMMARY, Vale de Cambra, Portugal
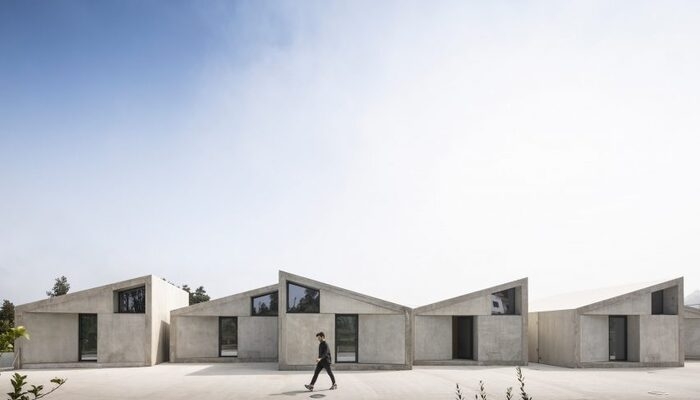

SUMMARY, an architecture firm in Portugal, utilised the cost-effective "Gomos System" to build this 10,743-square-foot mixed-use development in the Serra da Estrela mountains. The project features a floating tabletop covering a multi-service open space with six tube-like housing units. During its construction process, it optimises time and resources through efficient planning, quick assembly, and the use of concrete for both structuring and finishing.
2. CHARRIERE – 35 social housing units and shop by Mobile Architectural Office (MAO), Paris, France
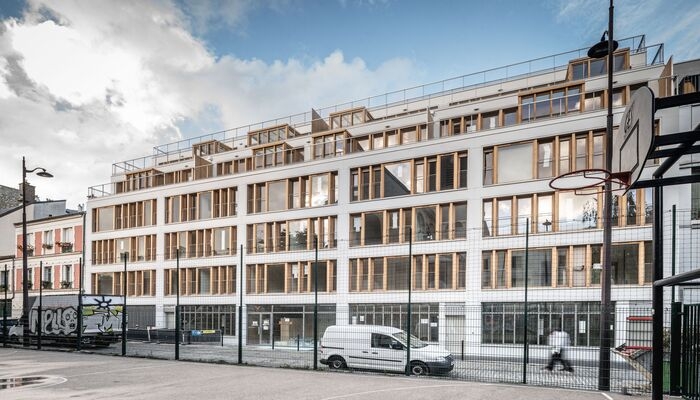

MAO's social housing project in the former Botelli workshop employs prefabrication to connect the past and present. Inspired by Parisian industrial architecture, the structure features precast concrete supports, slabs, and large timber trusses. The meticulous assembly of each element pays homage to the workshop's history as a cabinet-making facility.
3. Home-Office Pods AAND Sayana by Aaksen Responsible Aarchitecture, Bandung, Indonesia
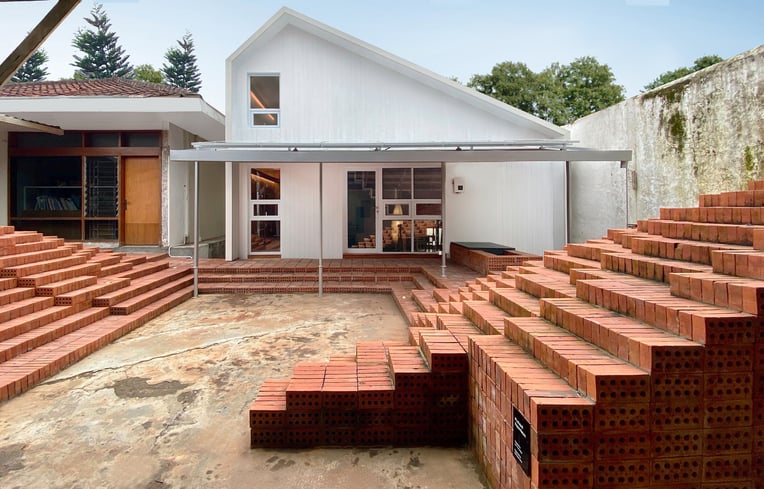

AAND Sayana is a modular home office designed to address the effects of the pandemic on workers. The building is equipped with on-grid solar panels for energy supply and can be easily built by anyone, regardless of experience, using high-quality, locally sourced prefabricated materials. It can be fully assembled in just three weeks and is constructed using strong, earthquake-resistant cross-laminated timber (CLT).
4. Homb by Skylab Architecture and Method Homes, Oregon, United States of America (USA)
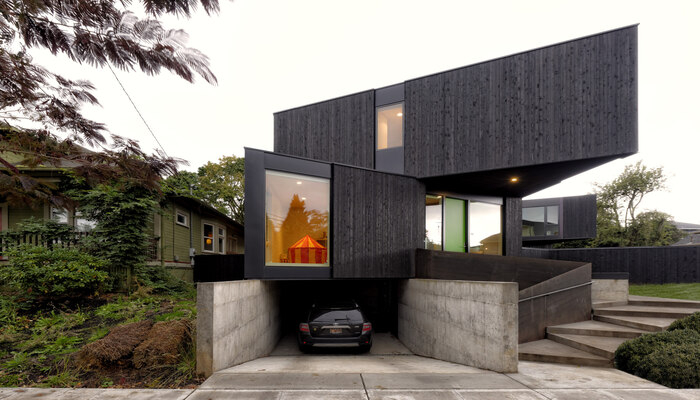

Skylab Architecture and Method Homes collaborated on HOMB, a modular and prefab building system in the Oregon region. It uses 100-square-foot triangle modules that can be adjusted on-site to create various shapes. The system is energy-efficient with insulation, solar-powered systems, and water conservation features. It reduces waste and uses sustainable materials, simplifying the design process and allowing for changes. The system works for both homes and large commercial buildings.
5. Dortheavej (Homes for All) by Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG), Copenhagen, Denmark
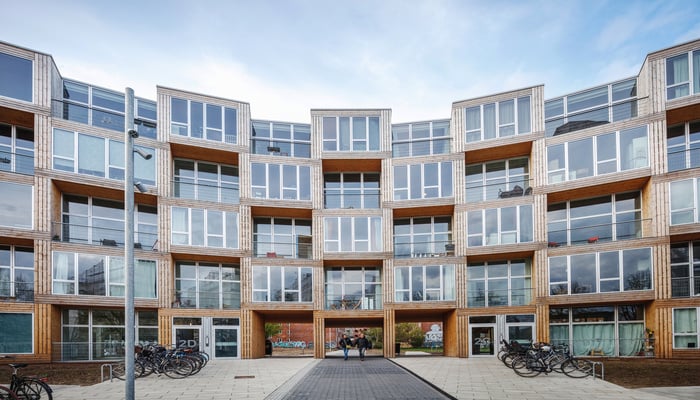

In 2013, BIG was commissioned by Lejerbo, a Danish non-profit housing association, to design Dortheavej, a project focused on affordable housing while maintaining pedestrian walkways and preserving green space. The Homes for All project features a distinct checkered pattern using a single prefab framework, curved to form a porous wall with a public plaza and a private green courtyard. The stacked modular dwellings along the curve provide each flat with a small terrace.
6. The Friends Lab House by AMPS Arquitectura & Diseño, Bentworth, United Kingdom
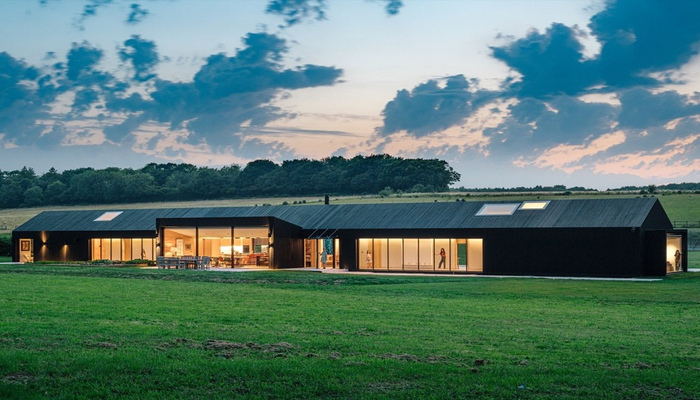

The purpose of ‘The Friends Lab House’ was to design a place where friends and family could spend their time near their main residence on the same farm. The Contra-laminated timber (CLT) method (where each layer of joined timber is placed perpendicular to the previous one) was used for its construction. The CLT method ensures great tensile and compressive strength. The on-site construction process of such a method lasts for a few days with almost zero waste generation.
7. Yellow House by Alejandro Soffia, Pucon, Chile
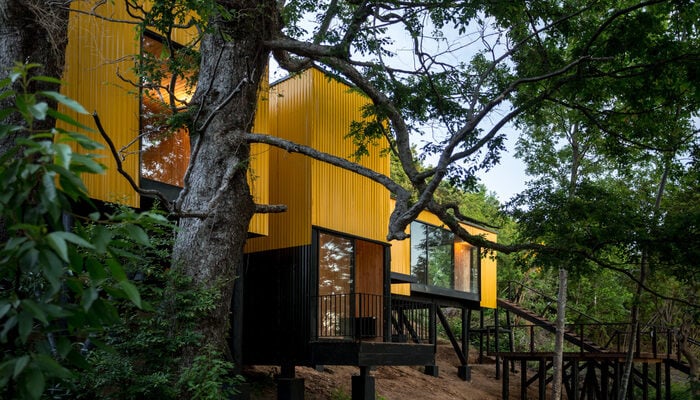

Inspired by the idea of building good quality structures having less impact on the surrounding environments, architect Alejandro Soffia has proposed a prefabrication strategy to build his projects. At the beginning of the project, a slab panel was chosen as a dimensional unit. These slabs were then used to create a volume to create a space with two slabs and two walls, after which the dimensions of the rooms were adjusted.
Read more: The Connection Between Art And Architecture: The Beauty of Synergy
8. No-Footprint House by A-01, Ojochal, Costa Rica
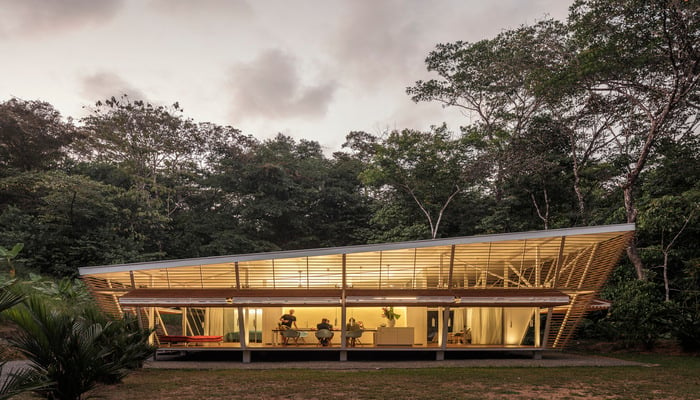

The prefabricated No-Footprint House is part of A-01's zero-carbon housing series. The timber facade panels of the building may be opened and closed, allowing for cross ventilation and good views. The zero-footprint attribute stems from the structure's use of materials that have a low environmental impact. In addition to this, this home is easily transportable on the back of a truck and can be constructed and disassembled as needed.
9. Desert House Prefab by Marmol Radziner, Desert Hot Springs, USA
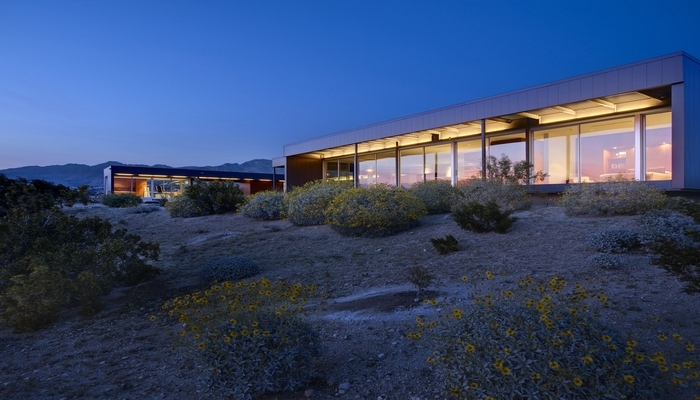

The Desert House, a prototype home by Marmol Radziner Prefab, is located in Desert Hot Springs, California. It spans five acres and features outdoor living areas that double the interior space. With a focus on capturing scenic views, the house comprises four house modules and six deck modules. The design seamlessly blends indoor and outdoor spaces, extending towards a guest house and studio. Prefabricated with steel framing, the modules can be clad in various materials and provide sun protection.
Read more: A Complete Guide to Building Modular Homes in 2025
10. Sonoma WeeHouse
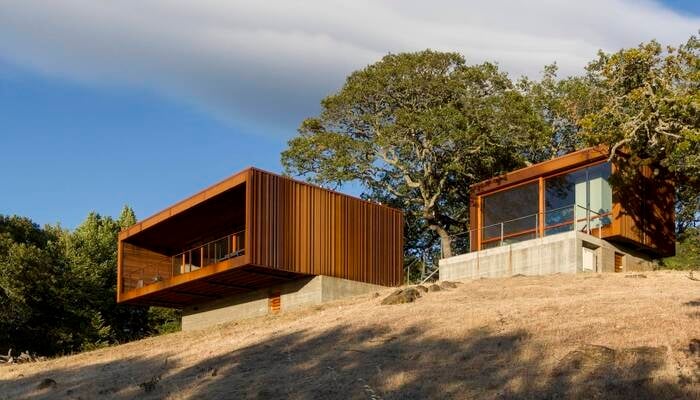

In the Sonoma Mountains, architects Geoffrey Warner and BJ Siegel created a prefab home that provides seamless views of the surrounding scenery with its glass walls. The construction involved pouring and preparing two concrete plinths, followed by the placement and fastening of two prefabricated cubes using a crane. The entire modular residence was completed in just one day, showcasing the efficiency of the construction process of a prefabricated structure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, modular and prefabricated homes are revolutionizing the housing industry by providing efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable architectural solutions. With their diverse designs, customizable options, and quality construction, these homes offer an enticing alternative to traditional site-built houses. As the demand for affordable and environmentally friendly housing grows, modular and prefabricated homes are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of housing.
Want to learn how to design prefabricated homes like these?
Explore Computation design course offered by Novatr. This course helps you understand the subject theory, master advanced tools, and build your expertise.
The course helps you:
- Become a BIM expert in just 9 months.
- Master 15+ BIM software and industry workflows.
- Learn from AEC professionals leading BIM at top-tier firms worldwide.
- Work on three capstone projects to practice your skills and enhance your portfolio.
- Get placement assistance to land jobs in globally operating BIM firms.
Visit our Resource page and level up your career in BIM today!

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!


.png)


-1.png)