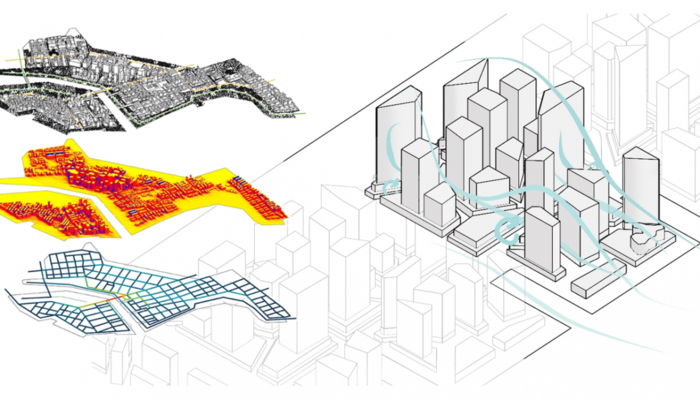
Why Parametric Landscape Design is the Next Big Thing in Landscape Architecture?

Table of Contents
The idea of “creative thinking” has gotten a new dimension with the advent of parametric modelling and design. Parametricism has established itself as the modern-day methodology of design conceptualisation, helping redefine what’s possible with technology in the built environment.
What is Parametric Modeling and Design?
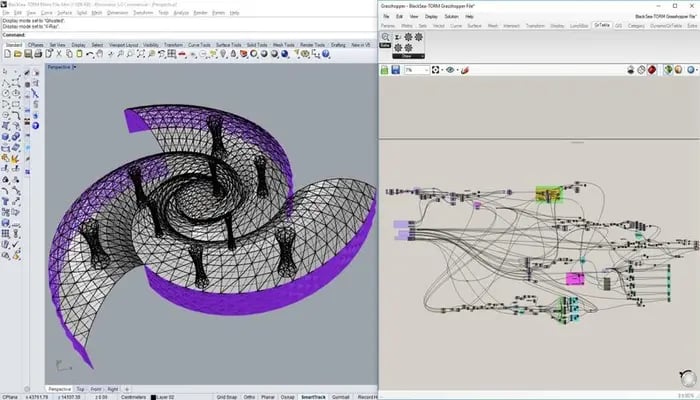
Parametric modelling is a computational design approach that involves creating 3D models by defining parameters and establishing relationships between them.
Further simplifying the concept, parameters are adjustable variables such as dimensions and angles that can be linked through algorithms, forming a set of rules that dictate the model’s behaviour. This process is completed through parametric modelling software such as Dynamo, Revit, Grasshopper, and Rhino. These software provide a comprehensive platform for defining, manipulating, and visualising building components to be composed as functional parametric designs.
What are the Benefits of Parametric Modelling and Design?
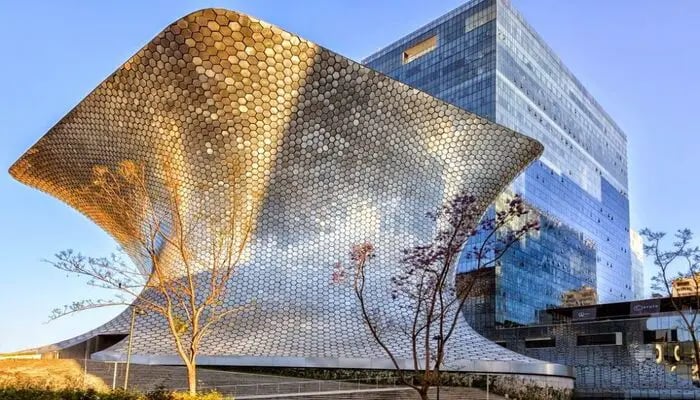

Parametric design architecture is shaping the buildings and infrastructure of tomorrow. But is there a way to derive real-world benefits from this new style of architecture? Below is a list of some features that show the importance of parametric design in modern architecture.
1. Design Exploration
Parametric modelling fosters a non-linear design process, encouraging architects to explore innovative and complex forms that might be challenging with traditional methods. Using algorithms and parameters often allows them to create intricate structures and patterns that respond to specific stimuli, advancing the design process into a new era of possibilities.
2. Optimised Performance
Architects and designers use parametric design to analyse and adjust parameters, allowing for the optimisation of structures based on performance criteria. These parameters include criteria like energy efficiency and structural integrity. This gives professionals a sense of control over the project.
3. Enhanced Collaboration
Parametric modelling and design also facilitate collaboration among architects, civil engineers, and other stakeholders. Parametric tools offer a shared platform for real-time design modifications. This enhances stakeholder communication while contributing to the ease of coordination in complex building systems.
4. Sustainable Solutions
Parametric modelling aids in the creation of environmentally conscious designs by enabling architects to simulate and optimise for factors such as sunlight exposure, wind flow, and thermal performance. This predictive capability enables them to make informed decisions that contribute to energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
5. Time and Cost Savings
The efficiency of parametric design can aid significant time and cost savings throughout the design and development phases. Rapid iterations, coupled with the ability to analyse performance and optimise designs, contribute to more streamlined and economical project timelines.
What is Landscape Architecture and Design?
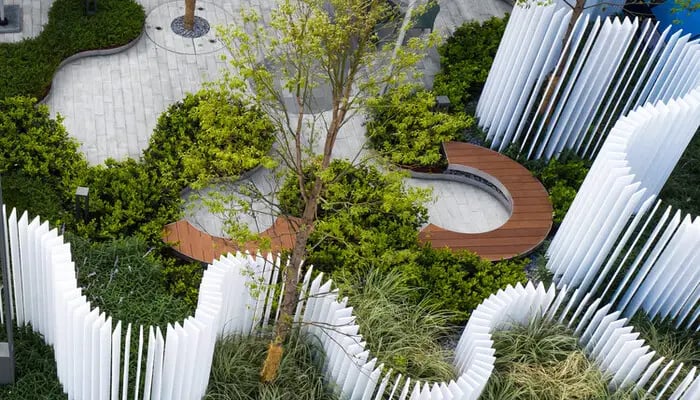

Landscape architecture is a multidisciplinary design field that combines elements of art, design, environmental science, and urban planning to create visually appealing, highly functional, and sustainable outdoor spaces. Some key examples of outdoor spaces include arenas, squares, parks, playgrounds, urban plazas, and waterfronts.
The professionals who design these places are called landscape architects. Their work goes beyond aesthetics and encompasses considerations like ecological sustainability, environmental conservation, and the enhancement of the quality of life for individuals and communities. They collaborate with other professionals, stakeholders, and clients to ideate and implement designs that harmonise with the natural surroundings while meeting the diverse needs of users.
What are the Applications of Parametric Design in Landscape Architecture?
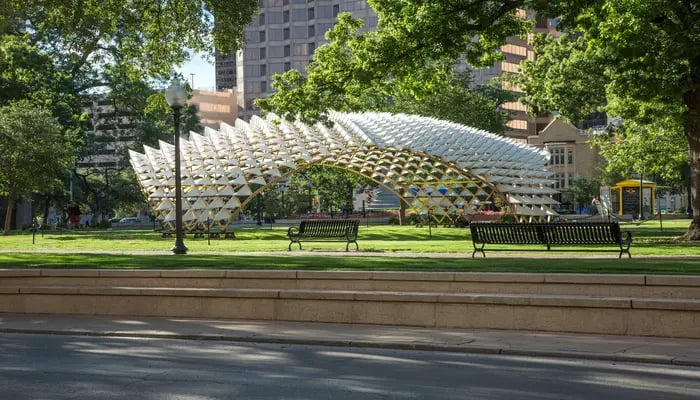

Through the lens of parametricism, outdoor spaces are canvases for dynamic transformation, allowing architects to sculpt landscapes with precision and purpose. Let us look at the five key applications of parametric design in landscape architecture.
1. Site Analysis and Planning
Parametric landscape design allows professionals to conduct a comprehensive site analysis by integrating geographical, climatic, and topographic data. The dynamic adjustment of parameters facilitates the optimisation of land use, ensuring that the landscape design is not only visually appealing but also responsive to the unique characteristics of each site. This includes factors such as sun exposure, wind patterns, and soil conditions, optimising the placement of elements like seating areas, pathways, and vegetation.
2. Creating Dynamic Structures
Landscape architecture involves planning and designing structures like pergolas, gazebos, and shaded walkways. By using parametric landscape design, architects can explore new structural forms, materials, and construction techniques to develop engaging designs. This helps in the realisation of complex geometries which are otherwise difficult to achieve. More so, parametric modelling helps devise pedestrian movement patterns to curate circulation pathways.
3. Generative Planting Design
Parametric tools enable generative design approaches for planting schemes. Algorithms can be employed to explore and generate diverse combinations of plant species based on ecological compatibility, aesthetics, and functional requirements. This promotes biodiversity within the landscape, creating resilient ecosystems that are not only visually appealing but also contribute to environmental sustainability.
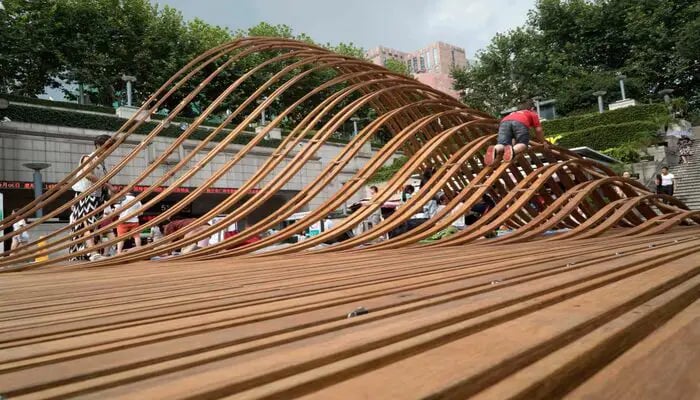

4. Microclimate Optimisation
The precision afforded by parametric landscape design tools extends to the optimisation of microclimates within outdoor spaces. By meticulous analysis of wind patterns, sunlight exposure, and thermal conditions, landscape architects can design areas that not only provide comfort but also diversify microclimates. This approach enhances the overall user experience, ensuring that outdoor spaces are attuned to the nuances of their immediate environment.
5. Water Management
Parametric landscape design is instrumental in the efficient water distribution and drainage in landscaped areas. Architects can model and analyse water flow by incorporating features like permeable surfaces, rain gardens, and dynamic water elements. Additionally, smart irrigation systems can be deployed to respond to real-time data. This facilitates the optimisation of water management strategies, ensuring sustainable water conservation practices.
7 Best Software for Parametric Landscape Design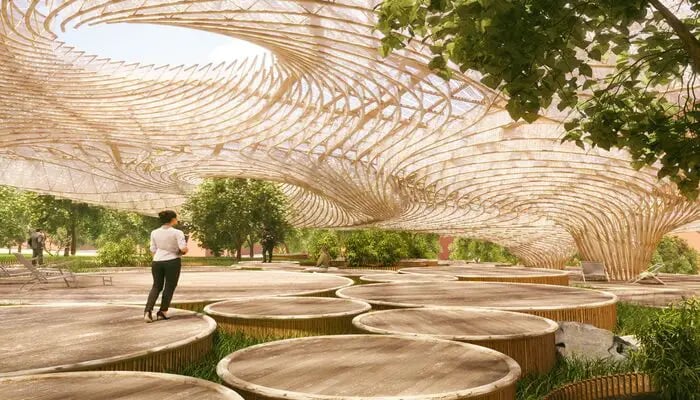
The realisation of parametric landscape design is facilitated by a varied suite of software. They help navigate the complexities of parametric design, offering a way to bridge conceptual ideas to dynamic and responsive environments that come to life. Let’s delve into the most useful and popular parametric modelling software for landscape architecture.
1. Real-Time Landscaping Architect
RealTime Landscaping Architect offers a user-friendly platform for landscape architects to bring their designs to life in real-time. With its extensive library of plants, hardscapes, and other elements, this software enables designers to create immersive 3D models of landscapes. It provides a real-time rendering feature that allows instant visualisation and modification of designs, making it an ideal tool for quick design iterations.
2. Dynascape
Dynascape caters specifically to landscape professionals, offering a suite of design, presentation, and client management tools. This software is compatible with AutoCAD and provides a robust platform for parametric landscape design. Dynascape's features include dynamic plant libraries, irrigation design, and the ability to create precise and detailed construction drawings, making it a comprehensive solution for landscape architects.
3. Land F/X with AutoCAD
Land F/X, a powerful plugin for AutoCAD, enhances the parametric design capabilities of this widely used drafting software. It provides specialised tools for plant selection, irrigation design, and site detailing. Its seamless integration with AutoCAD streamlines the design process, making it efficient and collaborative. Land F/X is particularly valuable for landscape architects working on intricate and data-rich projects.
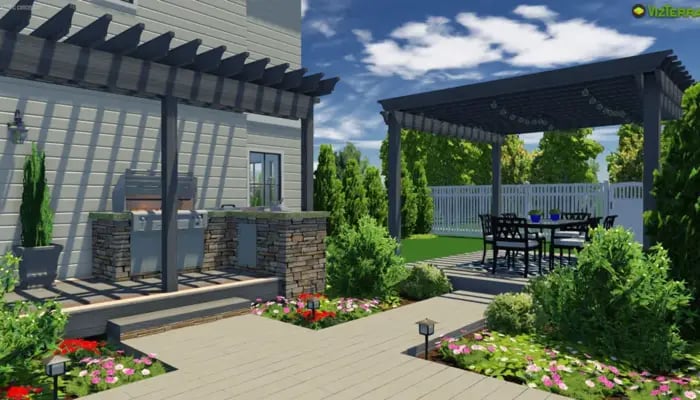
4. VizTerra
VizTerra stands out as a user-friendly software solution that empowers landscape architects to create stunning 3D visualisations of their designs. With its parametric landscape design and modelling tools, architects can sculpt terrains, design outdoor structures, and stimulate plant growth. VizTerra also offers features for client presentations, helping landscape professionals effectively communicate their ideas to clients and stakeholders.
5. Grasshopper
Grasshopper is a visual programming language plugin for Rhino which has become a staple in the parametric design toolkit. It allows designers to create complex algorithms that drive the generation of intricate and responsive designs. With Grasshopper's flexibility and adaptability, landscape architects can explore parametric design principles, automate repetitive tasks, and experiment with innovative geometries in their projects.
6. Plant Factory
Plant Factory specialises in the parametric design of vegetation, providing landscape architects with a dedicated tool for creating realistic and diverse plant models. This software enables designers to generate customisable 3D plant species, control growth parameters, and simulate plant behaviours.
7. Vectorworks
Vectorworks Landmark is a Building Information Modelling (BIM) software that integrates parametric landscape design tools into a comprehensive design environment. With Vectorworks, designers can create dynamic 2D and 3D models, generate planting plans, and optimise site designs with parametric elements. Its collaborative features and compatibility with industry-standard file formats make it one of the most popular parametric design software in the industry across the globe.
Parametric Landscape Design in Action
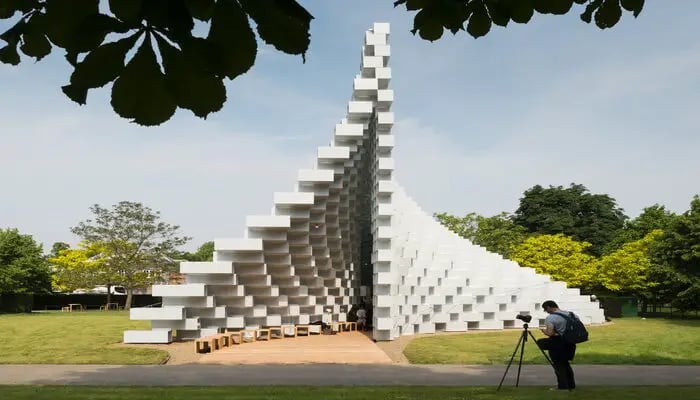

Situated at the Serpentine Gallery in Hyde Park, London, the Serpentine Pavilion serves as an annual architectural showcase, featuring the distinctive work of various architects. In 2016, Bjarke Ingels Group (BIG) took the helm, presenting a striking example of parametric landscape design. The pavilion’s design was a complex sculptural form that adhered to simple geometric rules, leveraging web technologies for its modelling.
Characterised by the pattern of an "unzipped wall," the structure’s design ingeniously splits a straight line of tubular fibreglass bricks into two undulating sides. This recurring brick geometry echoed the playful aesthetics found in Lego and Minecraft, while the overall structure exhibited the meticulous precision of an algorithm.
In Conclusion
As technology continues to advance and design boundaries are pushed, the integration of parametric principles will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of landscape architecture. The symbiosis between cutting-edge technology and parametric design not only enhances the efficiency of the architectural process but also paves the way for innovative solutions to complex challenges.
If you're keen to learn about parametric design and its applications in landscape architecture, we suggest you check out the Master Computational Design Course by Novatr. Throughout the course, you will learn 6+ software with 15+ plug-ins that can help you elevate your landscape designing skills to the next level.
Explore the course today.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!

%20(1).png)
%20(1).png?width=767&height=168&name=MCD%20B%20(Course%20Banner)%20(1).png)

.png)