A Closer Look at the Scope of BIM in Civil Engineering(2025)
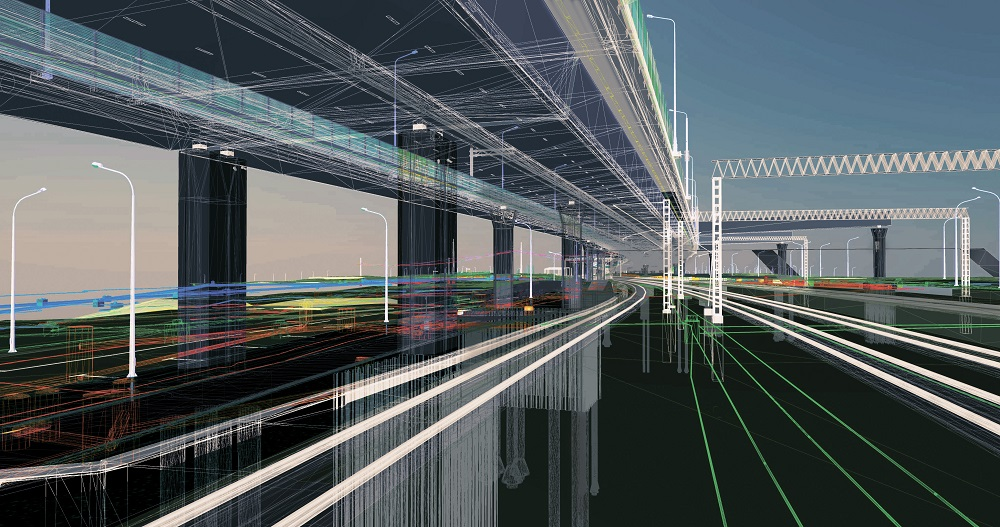

Table of Contents
The civil engineering landscape is ever-evolving; innovations, technological advancements, and sustainable practices are paving the way for a brighter future. Building Information Modelling (BIM) has emerged as a transformative force reshaping how construction and infrastructure projects are conceptualised, designed, constructed, and maintained. BIM is a paradigm shift that is transcending geographical boundaries and reshaping the global construction industry. From towering skyscrapers to sustainable infrastructure, the scope of BIM in civil engineering has reformed traditional practices, fostering innovation at an unmatched scale.
This comprehensive blog will talk about the multifaceted scope of BIM in civil engineering, its importance, famous BIM applications worldwide, and its scope in future infrastructure modelling. Let’s get started!
What is the significance of BIM in the Civil Engineering Industry?

Civil engineering is a profession that deals with the designing, construction, and maintenance aspects of infrastructure projects like roads, bridges, canals, dams, railways, and airports. Many civil engineers have a misconception that BIM is useful only for architectural projects and design purposes. However, the significance of BIM in civil engineering is profound and multifaceted, as such it has become a must-have skill for engineers to possess. To understand more about what BIM is in civil engineering, take a look at some key points highlighting the scope of BIM in civil engineering:
1. Conceptualisation
BIM helps create an intelligent 3D project model that provides a project’s holistic view. You can produce multiple conceptual designs of the infrastructure and evaluate them to detect clashes and conflicts in the preliminary design phase. This helps in transitioning the 3D model to a detailed design stage faster with greater precision.
Read more: Exploring the 8 Most Innovative BIM Projects in the Middle East
2. Detailed Designing
BIM software for civil engineers comes with a range of tools that you can use for detailed designing. For instance, tools such as cross-section views (SolidWorks) and components roads (InfraWorks) can help with advanced road design. Similarly, BIM tools can help effectively design alignments and add turn lanes, overpasses, and intersections in transportation projects. You can also use specialised analysis tools to check road styling and parking lot space for better subdivision layout concepts. In all, BIM in civil engineering projects facilitates better planning, designing, and structural analysis to enhance the accuracy and precision of the project.
3. Analysis and Simulations
BIM also helps in performing analysis and simulations on the 3D models. With different BIM tools, you can make better decisions for flood simulation, distance, dynamic site analysis, and more. For instance:
- Modelling different types of roadway and intersection configurations and simulating traffic to evaluate optimal design alternatives
- Providing stormwater management and incorporating light-rail corridors
4. Cost Reduction
With BIM, you can also design 4D (time management) and 5D (cost estimation) project models. With 4D in BIM, you can outline the phase wise project completion timeline and how the project will evolve over time. BIM also helps automate the estimation process and calculate future expenses with greater accuracy. The cost estimation includes costs of materials and prefabricated and modular elements, labour costs, and shipping costs. Furthermore, BIM can also help optimise expenses by comparing different materials for cost-effectiveness.
5. Collaboration and Communication
BIM facilitates collaboration among all stakeholders involved in a project – architects, engineers, contractors, and others. BIM is a collaborative process that provides a centralised digital platform that fosters a collaborative environment for better communication and coordination. This reduces errors and conflicts and aids in better decision-making.
6. Clash Detection
Clash detection is a crucial part of the BIM modelling process. It helps speed up project timelines by identifying potential clashes between several project components. By detecting clashes during the design phase, you can eliminate the chances of multi-level design changes during the construction phase, which can lead to delay in project completion. Notably, making changes during the construction phase are costly as well.
Why is it Important for a Civil Engineer to Know About BIM?
BIM has become an integral part of modern civil engineering practices and engineers who possess BIM skills are well-equipped to design, plan, and manage projects efficiently and cost-effectively. They can collaborate with interdisciplinary teams and meet the ever-evolving demands of the industry. Read on to learn the importance of BIM in civil engineering:
- Efficiency in Design and Planning: BIM enables you to create detailed multidimensional models of infrastructure projects with more precise project design and planning. This optimises designs, reduces errors, and improves project efficiency.
- Improved Collaboration: With BIM, all stakeholders can work on a single model simultaneously, improving collaboration and coordination among multiple stakeholders. This, in turn, reduces time and results in smoother project execution.
- Project Visualisation: BIM allows you to create a project’s realistic 3D visualisations. This helps convey complex engineering concepts to clients and regulatory authorities, making it easier to get approvals and funding for projects.
- Sustainability Integration: Green and sustainable building is the new trend in the industry. You can employ BIM to assess and optimise the environmental sustainability of infrastructure projects. BIM tools aid in designing eco-friendly structures, considering factors like energy efficiency and environmental impact.
- Facility Management: BIM models can be efficiently used for facility management and as-built documentation. After the construction phase, 3D models can be used to track the conditions of infrastructure elements, plan maintenance, and optimise operations for long-term sustainability.
- Competitive Advantage: Today’s job market is highly competitive, and you must possess most of the required skills to remain competitive. Many employers in the industry prefer BIM-skilled candidates, and thus learning BIM can enhance your career prospects and earning potential.
- Global Adoption: BIM is becoming a global standard in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry. Civil engineers who are proficient in BIM can work on projects worldwide, paving the way for a global career.
Famous Applications of BIM Around the World: Case Studies
BIM has found its application in numerous high-profile construction projects around the world, transforming the way these projects were designed, planned, and executed. These projects are an example of how BIM has become an indispensable tool in the industry and is helping to deliver iconic and complex projects with improved efficiency, collaboration, and cost-effectiveness. Take a look at some famous case studies showcasing the use of BIM:
1. Museum of the Future, Dubai

Dubai’s Museum of the Future has a complex design structure, where BIM played a crucial role. 4D BIM algorithms were used to create the torus design of the museum, substantially saving time and money during the construction phase. Architects and engineers used Tekla BIMSight, Autodesk Revit, and Dynamo for design and construction across the construction life cycle. BIM algorithms were also used to work through the conflicts in the façade, structure and Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (MEP) systems. Parametric scripting, along with Building Performance Simulation, helped the stakeholders achieve the LEED Platinum Certification.
Read more: How is BIM Used in Urban Planning in 2024?
2. Heathrow Terminal 5, London
Heathrow Terminal 5, London is the United Kingdom’s largest and most complex construction project. BIM was applied to coordinate the work of over 60 design firms and 15,000 workers. BIM application helped detect clashes, streamline workflows, and improve project communications.
3. Burj Khalifa, Dubai

The tallest skyscraper in the world, Burj Khalifa used BIM extensively in its construction. Engineers used the BIM software ETABS to create the mathematical model of the Burj Khalifa. BIM played a crucial role in managing the complex geometry of the tower, optimising its design, and coordinating between thousands of construction workers, and suppliers.
4. The Shard, London

London’s iconic tower, The Shard, was built using GEOBIM solutions across the entire construction life cycle. BIM was used to plan, design, and construct the 95-story skyscraper. GPS and GPR solutions, 3D laser scanners, and BIM and 4D project management software were used to improve construction productivity, and manage and maintain the building sustainably.
5. Singapore Sports Hub, Singapore

The Singapore Sports Hub is a state-of-the-art sports and entertainment complex. BIM played a pivotal role throughout its design and construction lifecycle. During the design phase, architects and engineers used BIM to create detailed 3D models to ensure a seamless integration of various components. BIM was also employed to support the sustainability goals and optimise the environmental performance of the building.
6. Fulton Center, New York City, USA

New York’s Fulton Center is a major transportation hub in the city. BIM was applied to renovate, modernise, and expand its transit facility while ensuring zero to minimal disruption to commuters. With its intricate design and integration of multiple subway lines, BIM was used for clash detection and resolution, minimising errors and costs and enhancing project scheduling.
7. The Louvre Abu Dhabi, Abu Dhabi, UAE
.jpg?width=708&height=347&name=The%20Louvre%20Abu%20Dhabi%20(1).jpg)
Louvre Abu Dhabi, an art museum, has a complex geometric dome structure, where BIM plays a crucial role. BIM was used in visualising and refining the intricate dome details and coordinating architectural, structural, and Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems. Moreover, the structure’s innovative rain-of-light effect was also made possible with the help of BIM.
Scope of Building Information Modelling in Civil Engineering
BIM has reconstructed the way structures are conceived, designed, constructed, and managed. The scope of BIM in civil engineering extends across the entire life cycle of a project, offering a holistic and data-rich approach.
During the design phase, engineers use BIM to create detailed 3D models of the project for visual aspects and to check the functional and behavioural characteristics of the structure. The digital representation also serves as a collaborative platform where interdisciplinary teams can communicate in real-time and detect clashes in the design phase. This ensures all the systems, from structural to electrical, align seamlessly. BIM also finds its application during the construction phase as it supports accurate quantity takeoffs, precise scheduling, and safety planning. In all, it contributes to cost control and timely project delivery.
During the post-construction phase, BIM serves as a powerful facility management tool. It provides the facility management team with an as-built project model, offering a detailed view of the structure, its components, and performance data. This aids in energy optimisation, structure maintenance, and timely renovations.
Beyond construction projects, BIM is also used in urban planning, infrastructure development, and disaster management. As the BIM technology continues to evolve, its role in digital twins and smart cities will expand. With emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), BIM is poised to redefine the construction and infrastructure industry, enhancing innovation, efficiency, and sustainability.
BIM for Future Infrastructure Development
The future of infrastructure development is fundamentally tied to BIM. As the cities expand and the global population grows, the demand for efficient, sustainable, and resilient infrastructure will also grow. BIM will help meet these demands efficiently as it offers a holistic approach to plan, design, construct, and maintain projects. Future development projects will use BIM to create digital twins, where every element is represented in detail, aiding in comprehensive analysis, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring of the projects. This, in turn, will enhance the overall productivity and longevity of the projects.
The future of BIM will also see its integration with emerging technologies like AI and IoT. This will bring a new era of smart infrastructure. With BIM in the application, you can also anticipate intelligent transportation systems that optimise traffic flow, self-monitoring grids that respond to demand fluctuations independently, and buildings that respond and adapt to different environmental conditions.
BIM will also help in making well-informed decisions, ensuring all projects are designed efficiently with a forward-looking perspective, considering their long-term performance, resilience to climate change , and adaptability to urban needs.
Read more: Uncovering the Significant Role of BIM in Constructing the Fehmarnbelt Tunnel
Conclusion
Conclusively, we can say the scope of BIM in civil engineering is wide-reaching and transformative. From being a mere visualisation and drafting tool to serving as the backbone of the industry, BIM has come a long way. It fosters collaboration between multiple teams, enhances precision, and reduces errors. Many countries are using BIM to plan, design and construct infrastructure projects, from the initial concept phase to the construction phase.
Furthermore, with its integration with technologies like AI and IoT, BIM’s potential continues to expand. This synergy will revolutionise the way civil engineering projects are planned, designed, and managed.
If you are wondering how you can become a BIM-skilled civil engineer, don’t worry. Novatr has got you covered! Enrol for Novatr’s 7-month long BIM course for civil engineers and get access to tools, technology, industry expertise, capstone projects, and mentors to grow your career. With practical and interactive modules, get a comprehensive learning experience that will keep you ahead of the curve in this rapidly evolving industry.
Head to our recourses page to learn more about BIM for civil engineers and get industry insights.

 Thanks for connecting!
Thanks for connecting!




.png)